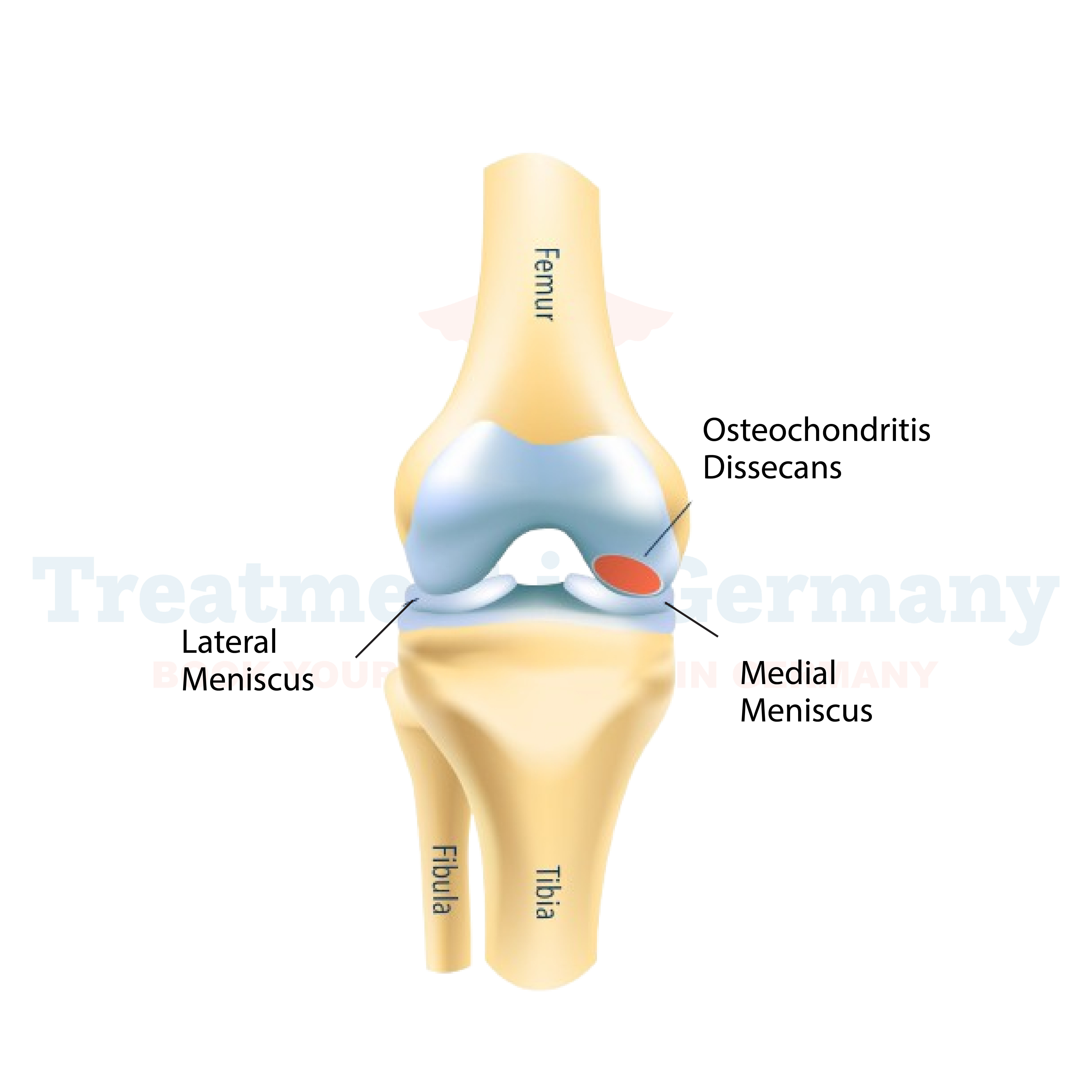
What is Osteochondritis Dissecans?
Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD) is a joint condition where a fragment of bone and cartilage separates from the joint surface.
This separation can occur due to reduced blood flow to the affected area, leading to the formation of a loose fragment within the joint.
Side Effects of Osteochondritis Dissecans
Patients with Osteochondritis Dissecans may experience several symptoms, including:
- Pain: Persistent pain in the affected joint, especially during movement or weight-bearing activities.
- Swelling: Swelling and tenderness around the joint, often accompanied by stiffness.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Difficulty in fully extending or bending the joint.
- Joint Instability: A feeling of the joint "locking" or catching during movement.
If left untreated, Osteochondritis Dissecans can progress, potentially leading to joint degeneration and osteoarthritis in the long term.
How is Osteochondritis Dissecans Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Osteochondritis Dissecans typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies:
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination by a healthcare provider to assess symptoms, joint stability, and range of motion.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), or CT (Computed Tomography) scans are commonly used to visualize the affected joint and identify any loose fragments or changes in bone structure.
Potential Treatment of Osteochondritis Dissecans
Treatment for Osteochondritis Dissecans depends on various factors, including the size and location of the lesion, patient age, and activity level. Common approaches include:
Non-Surgical Treatment:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms and modifying daily activities to reduce stress on the joint.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles around the joint and improve range of motion.
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Surgical Treatment:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery to remove or stabilize the loose fragment, stimulate healing, or repair the affected area of the joint.
- Osteochondral Grafting: Transplanting healthy cartilage and bone tissue to replace damaged areas in the joint.
- Joint Replacement: In severe cases of joint degeneration, joint replacement surgery may be necessary.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
