Pelvic fracturesare very severe injuries and any delay in diagnosis and management should be discouraged. Germany is well-known for its good healthcare and various effective solutions for such disorders as pelvic fractures. Modern technologies, as well as many certified specialists, allow Germans to receive high-quality treatment for such a disease.
What are pelvic fractures?
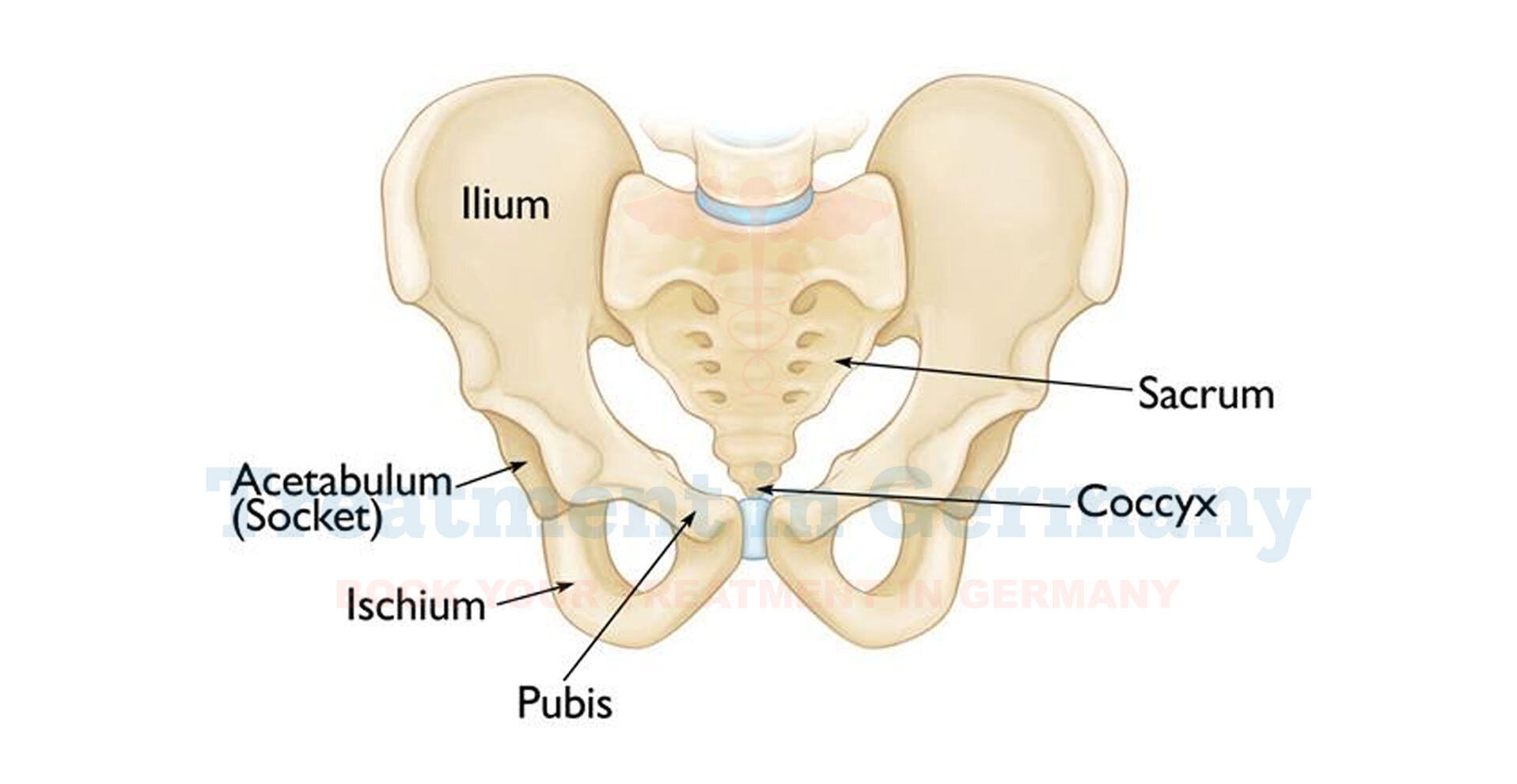
Pelvic fractures are defined as the breakdown of one or several of the bones that make up the pelvis. The pelvis is a firmly built region consisting of the hip, sacral, and coccygeal bones, as well as some portions of the lumbar region of the vertebral column. In this respect, it supports and protects organs and tissues, including blood vessels and the lining of the gastrointestinal tract.
Types of Pelvic Fractures
Pelvic fractures are categorized based on their severity and the underlying injury mechanism:
Stress Fractures
They are a result of repetitive stress or pressure and they are common in athletes. Localized pelvic pain is a common consequence of these fractures in the older population.
Avulsion Fracture
An avulsion fracture occurs when a tendon or ligament pulls away, taking some bone with it. It is more frequent in young people, particularly sportspersons.
Symptoms of Pelvic Fractures
Symptoms of pelvic fractures depend on the severity but often include:
If these symptoms occur, this suggests that there could be a nerve, blood vessel, or organ injury nearby that needs emergency treatment.
Diagnosis of Pelvic Fractures
The severity of the injury requires an assessment, as it depends on an accurate diagnosis. German healthcare facilities utilize advanced diagnostic tools for evaluating pelvic fractures:
X-rays
Fractures are diagnosed with x-rays and the images of the pelvic bones bring out the break as a first line of diagnosing the condition.
CT Scan
A CT scan is a less invasive form of scan that provides a better picture by taking a number of X- ray images at the same time. In addition, the imaging assists doctors in gauging the purity and the level of difficulty of the fracture that is present.
MRI
Such examinations are applied when it is required further investigation of the state of soft tissues or suspicious cells. It is especially useful when it comes to diagnosing occult injuries or even fractures.
Treatment Options for Pelvic Fractures in Germany
There are different types and severities of pelvic fractures, and treatment in Germany varies according to this classification. Many hospitals exist in Germany, and they possess good equipment and qualified surgeons who can perform numerous procedures.
Conservative Treatments for Stable Fractures
Mild or stable fractures do not require surgery and are typically treated with:
Surgical Interventions in Severe Fractures
The types of fractures are mostly unstable, which is why surgical treatment is needed. Germany's hospitals employ advanced surgical techniques, including:
External Fixation
This process entails the placement of metallic rods or screws in the pelvic bone and these lead to metallic bars outside the body. It supports the pelvis while it is being healed.
Skeletal Traction
A pulley system is utilized to modify the alignment of the bones. Pins are inserted inside the thighbone to maintain its proper position.
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)
In ORIF, a surgeon has to align the fractured bones back and fix them with the use of plates and screws. This technique helps to align it properly and stabilize it as well.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Orthopedic mobilization is crucial in the management of pelvicalyceal fracture as it helps to achieve the over-mobility and strength of muscles. Many of Germany’s medical centers focus on rehabilitation and enhancing patient recovery, hence effective programs.
Walking Aids
During this particular period, the patient needs a pair of crutches, a cane, or any other appliance that helps them abstain from stressing the pelvis.
Physical Therapy
Physiotherapy assists patients on how to gain strength and moving around, especially for the disabled or those in pain. Some of the exercises that have been suggested are targeted at strengthening the pelvis and in an effort to eradicate complications.
Managing Complications
Post-treatment care in Germany includes monitoring for complications such as:
Innovative Treatments in Germany
A country that has shown massive advancement in how they manage pelvic fractures is Germany. Teaching hospital technologies include mechanical aid in surgeries, specifically robotic surgeries, and 3D imaging in the operating room. Germany’s healthcare providers have embarked on the adoption of new strategies that would help to bring down the recovery period.
Why choose Germany for pelvic fracture treatment?
Germany’s medical industry is recognized as being one of the best; therefore, the availability of recognized and professional pelvic fractures makes people opt for Germany. Key factors include:
Preventing Pelvic Fractures
Preventing pelvic fractures involves adopting safety measures, especially for at-risk individuals:
Frequently Asked Questions
In Germany, how are pelvic fractures diagnosed?
Pelvic fracture is usually diagnosed using imaging surveys such as X-rays, CT sections, and MRI for better assessment.
Which types of pelvic fractures are treated in Germany?
Hospitals in Germany manage all types, including closed fractures, stress, avulsions, and those that are unstable and need surgery.
What is the duration of a hospital stay after a pelvic fracture?
Healing usually occurs within two months, but this will depend on the extent of the fracture and the chosen mode of therapy.
Which are the available innovative treatments within Germany?
Out of the medical treatments used in Germany, the most popular ones include robot surgeries, computerized tomographies, and detailed fixing methods for operations.
What are the risks of complications associated with pelvic fractures?
Some of the side effects of the treatment are blood clotting, chronic pain, sexual dysfunction, and deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and these are well dealt with in Germany.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
