Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Treatment in Germany
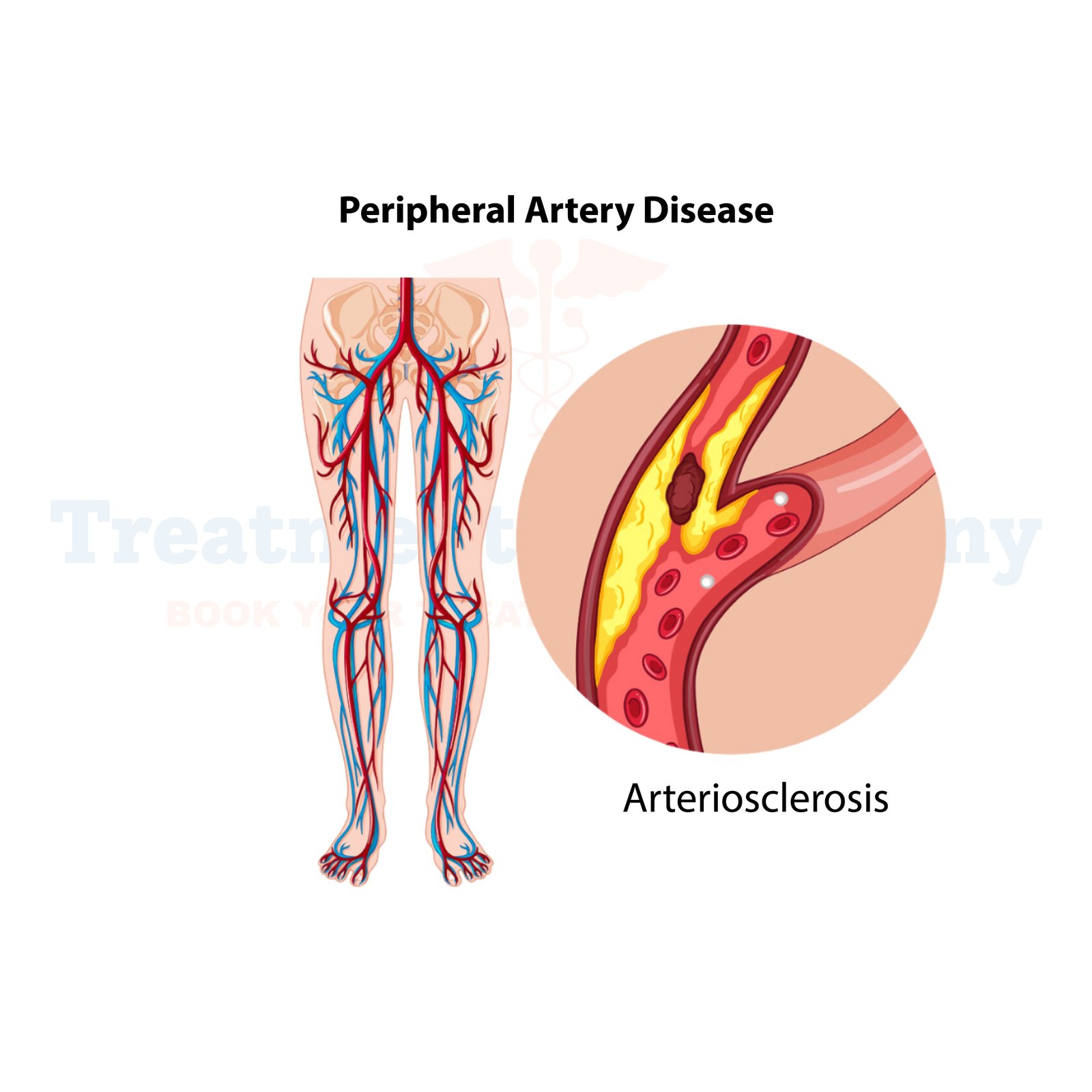
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a common circulatory condition where the arteries that carry blood to the limbs become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This condition typically affects the lower limbs and leads to poor circulation, resulting in pain, cramping, and in severe cases, tissue damage.
PAD can significantly impact a person's quality of life and, if left untreated, may lead to complications such as ulcers, gangrene, or even amputation. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing PAD effectively, and Germany offers advanced and innovative treatments to help patients lead active, pain-free lives.
Introduction to PAD and Its Treatment in Germany
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) affects millions of people globally, with a higher prevalence in those over the age of 50. The condition results from the gradual buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the arteries, leading to their narrowing or blockage. PAD restricts blood flow to the legs, causing symptoms such as leg pain and cramps, especially during physical activity.
In Germany, treatment for PAD is considered some of the best in the world due to the country’s renowned medical expertise, advanced diagnostic tools, and a wide array of treatment options, ranging from lifestyle changes to advanced surgical procedures. Germany’s healthcare system focuses on early detection, innovative therapies, and comprehensive patient care, offering a holistic approach to managing PAD.
Types of Peripheral Artery Disease
PAD can affect different areas of the body, and its presentation may vary. The types of PAD include:
- Lower Limb PAD: The most common form, affecting the arteries in the legs and feet. It often results in pain and cramping in the lower limbs, particularly during walking or exercise.
- Upper Limb PAD: Less common than lower limb PAD, this form affects the arteries in the arms and hands, causing symptoms like numbness and discomfort.
- Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI): A severe form of PAD characterized by extreme reduction in blood flow to the limbs, leading to chronic pain, non-healing wounds, or even gangrene.
Each of these types requires a specific treatment approach, ranging from lifestyle changes to advanced surgical interventions.
Risk Factors for Peripheral Artery Disease
Several risk factors can contribute to the development of PAD, including:
- Obesity: A high body mass index (BMI) increases the likelihood of PAD due to excess fat contributing to the narrowing of arteries.
- Diabetes: Elevated blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of PAD.
- High Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia): Excess cholesterol in the bloodstream contributes to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of blockages.
- Smoking: Tobacco use accelerates the development of atherosclerosis, the leading cause of PAD.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can damage the arteries over time, increasing the risk of PAD.
- Age: PAD is more common in people over 50, particularly those with other risk factors.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus can contribute to inflammation and increased risk of PAD.
Symptoms of Peripheral Artery Disease
The symptoms of PAD can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the disease. Common signs include:
- Intermittent Claudication: Pain or cramping in the legs, especially during physical activity, which typically subsides with rest.
- Leg Fatigue or Weakness: A feeling of heaviness or tiredness in the legs during normal activities.
- Cold or Numb Feet: Reduced blood flow can cause a sensation of coldness or numbness in the feet and toes.
- Slow-Healing Wounds: Non-healing sores or ulcers on the feet or legs are often a sign of poor circulation.
- Shiny or Thin Skin: As blood flow decreases, the skin may become thin, shiny, or even develop a pale appearance.
In more severe cases, PAD can lead to tissue death (gangrene), requiring amputation if not treated in time.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools for PAD
Diagnosing PAD early is critical for preventing complications. Germany’s healthcare system is equipped with advanced diagnostic tools to accurately detect PAD:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are used to assess cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, and markers of inflammation, all of which can contribute to PAD development.
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): This non-invasive test compares the blood pressure in the ankle with that in the arm to determine the severity of PAD.
- X-rays: X-rays may be used to rule out other conditions affecting the limbs or to detect bone abnormalities in severe cases.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI provides detailed images of the blood vessels, helping doctors locate blockages or narrowing in the arteries.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: A CT angiogram is a non-invasive method to assess blood vessel health and locate areas of obstruction or narrowing.
- Ultrasound: Doppler ultrasound is commonly used to check blood flow and detect any blockages in the arteries.
These diagnostic tools ensure precise identification of PAD and the extent of arterial damage, allowing doctors in Germany to tailor treatment plans accordingly.
Treatment in Germany
Germany provides comprehensive treatment options for managing PAD, with a focus on improving circulation, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications. Treatment options include:
- Medications: Medications such as blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and antihypertensive medications are commonly prescribed to manage risk factors and prevent further artery narrowing.
- Angioplasty: A minimally invasive procedure where a balloon is inflated inside the blocked artery to widen it, restoring blood flow. In some cases, a stent is inserted to keep the artery open.
- Bypass Surgery: When angioplasty is not feasible, surgeons may perform bypass surgery, where a healthy artery or vein from another part of the body is used to bypass the blocked artery.
- Endarterectomy: A surgical procedure to remove plaque from the arteries to restore proper blood flow.
- Amputation: In severe cases of PAD where gangrene has developed, amputation may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection.
- Physical Therapy: Exercise programs are often prescribed to improve circulation, strengthen muscles, and reduce symptoms of PAD.
- Pain Relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other pain relievers may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort from PAD.
Why is it Preferable to Get Treatment in Germany?
Germany is one of the world’s leading countries in vascular medicine and treatment for PAD. Patients from around the world seek treatment in Germany for several reasons:
- Innovative Treatment in Germany: The country is home to some of the most advanced medical technologies and innovative treatment options, ensuring effective management of PAD.
- World-Class Hospitals in Germany: German hospitals are equipped with the latest medical technologies and are known for their high standards of care.
- Doctors and Surgeons in Germany: Doctors and vascular surgeons in Germany are highly skilled and experienced, specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of PAD.
- Comprehensive Approach: Germany offers a holistic approach to PAD treatment, incorporating physical therapy, complementary therapies, and lifestyle changes alongside advanced medical treatments.
Conclusion
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a serious condition that requires early diagnosis and intervention to prevent severe complications. Germany provides cutting-edge treatment options, advanced diagnostic tools, and a team of specialists who offer personalized care for PAD patients. Whether through non-invasive therapies, surgical interventions, or complementary treatments, the country’s healthcare system ensures that PAD patients receive the best possible care.
With state-of-the-art hospitals, innovative treatments, and a multidisciplinary approach, Germany stands out as a global leader in PAD treatment, providing patients with the opportunity for better circulation, improved quality of life, and long-term health.
👉 Contact us for
further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
