Peripheral Nerve Injury Treatment in Germany
Peripheral Nerve Injuries occur when nerves outside the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to impaired movement, sensation, or organ function. These injuries may result from trauma, inflammation, or other medical conditions, and they can severely impact daily life. Germany has earned a global reputation for its advanced healthcare system, offering innovative treatments for Peripheral Nerve Injuries. Equipped with cutting-edge technology, world-class specialists, and a multidisciplinary approach, hospitals in Germany ensure high success rates for nerve repair and recovery.
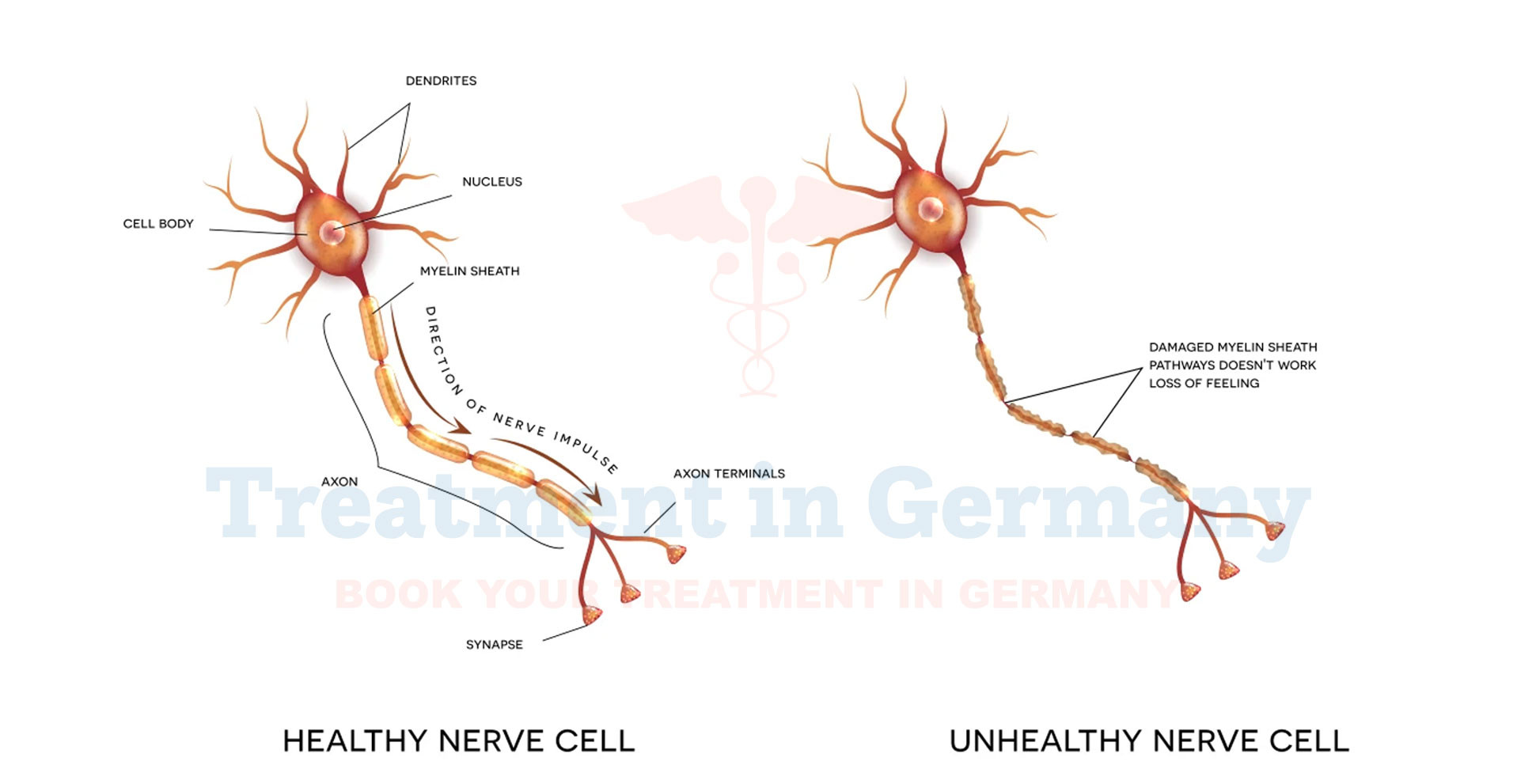
Peripheral Nerve Injuries (PNIs) involve damage to the nerves responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. This damage can disrupt motor, sensory, or autonomic functions, depending on the severity and location of the injury. Causes range from accidents, infections, or autoimmune diseases to complications arising from diabetes or obesity. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to restoring nerve function and preventing long-term complications.
Germany offers some of the most advanced diagnostic and treatment facilities for PNIs, providing a comprehensive approach that includes surgical interventions, physical therapy, and innovative regenerative therapies.
Types of Peripheral Nerve Injury
Peripheral Nerve Injuries are categorized based on the severity and mechanism of nerve damage:
Neuropraxia:
The least severe type, where nerve conduction is temporarily blocked without structural damage.
Symptoms usually resolve within weeks.
Axonotmesis:
- Partial damage to the nerve fibers, affecting signal transmission but leaving the surrounding structures intact.
- Recovery may take months, depending on the extent of damage.
Neurotmesis:
- The most severe type, involving complete nerve disruption.
- Requires surgical intervention for repair.
Compression Neuropathy:
- Occurs due to prolonged pressure on a nerve, leading to symptoms such as numbness or weakness.
- Common examples include carpal tunnel syndrome or sciatica.
Risk Factors for Peripheral Nerve Injury
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing Peripheral Nerve Injuries, including:
- Trauma or Accidents: Physical injuries such as fractures, dislocations, or lacerations can damage nerves.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels over time can lead to nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy).
- Obesity: Increased body mass index (BMI) can put pressure on nerves.
- High Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia): Excess cholesterol can restrict blood flow to nerves, leading to damage.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus or Guillain-Barré syndrome can cause inflammation, affecting nerve function.
- Repetitive Strain: Continuous repetitive motions can lead to nerve compression or injury.
Symptoms of Peripheral Nerve Injury
Symptoms vary depending on the type and location of the nerve injury but commonly include:
- Numbness or Tingling: Often described as a "pins and needles" sensation.
- Muscle Weakness: Difficulty in performing daily tasks due to reduced strength.
- Loss of Sensation: Inability to feel heat, cold, or touch in affected areas.
- Burning Pain: Persistent pain that worsens during activity.
- Paralysis: Severe cases may lead to loss of movement in the affected region.
- Muscle Atrophy: Prolonged nerve damage can result in shrinking of the muscles.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Early and accurate diagnosis of Peripheral Nerve Injuries is essential to determine the severity and guide treatment. In Germany, hospitals use state-of-the-art diagnostic tools, including:
- Blood Tests: Identify underlying conditions like diabetes or autoimmune diseases contributing to nerve damage.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures electrical activity in muscles to assess nerve function.
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): Determines the speed and strength of nerve signals.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of soft tissues and nerves, helping detect inflammation or compression.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Useful for identifying bone fractures or structural abnormalities affecting nerves.
- Ultrasound: Offers real-time imaging of nerves, particularly for compression-related injuries.
Treatment in Germany
Germany is renowned for its innovative treatment options and comprehensive approach to Peripheral Nerve Injuries. The treatment plan is tailored to the severity of the injury and may include:
Medications
- Pain Relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or stronger medications are prescribed for managing nerve pain.
- Corticosteroids: Used to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms in autoimmune-related nerve injuries.
Surgical Interventions
- Nerve Repair Surgery: Reconnects severed nerve ends to restore functionality.
- Nerve Grafting: In cases of severe damage, a healthy nerve from another part of the body is transplanted to bridge the gap.
- Decompression Surgery: Alleviates pressure on compressed nerves, as seen in conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
Innovative Therapies
- Stem Cell Therapy: Encourages regeneration of damaged nerve tissues by using stem cells.
- Dendritic Cell Therapy: A regenerative treatment that boosts the body’s immune response to aid nerve recovery.
- Neurostimulation: Devices like spinal cord stimulators are used to manage chronic nerve pain.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Customized exercises supervised by physical therapists help restore muscle strength, improve mobility, and reduce pain. Complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, are integrated to enhance recovery.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes: Managing diabetes and cholesterol through a balanced diet to support nerve health.
- Smoking Cessation: Reduces further damage to blood vessels and nerves.
Why is it Preferable to Get Treatment in Germany?
Germany is a global leader in the treatment of Peripheral Nerve Injuries due to its combination of expertise and advanced medical facilities:
- Innovative Treatment in Germany: Cutting-edge therapies such as stem cell treatments and minimally invasive surgeries are widely available.
- Hospitals in Germany: Renowned for their world-class infrastructure and patient-centered care.
- Doctors and Specialists in Germany: Experienced professionals with expertise in diagnosing and managing complex nerve injuries.
- Holistic Approach: Treatments are complemented by physical therapy, dietary guidance, and lifestyle adjustments for comprehensive care.
- High Success Rates: German healthcare facilities boast impressive outcomes for nerve repair and recovery.
Conclusion
Peripheral Nerve Injuries can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, but timely diagnosis and treatment can lead to remarkable recovery. Germany’s advanced medical infrastructure, expert specialists, and innovative therapies make it a preferred destination for Peripheral Nerve Injury treatment. Whether it’s through surgical interventions, regenerative medicine, or rehabilitation, German healthcare providers ensure personalized care tailored to each patient’s needs.
By choosing treatment in Germany, patients benefit from cutting-edge medical advancements, a multidisciplinary approach, and a commitment to restoring nerve function and improving overall well-being.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
