Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Treatment in Germany
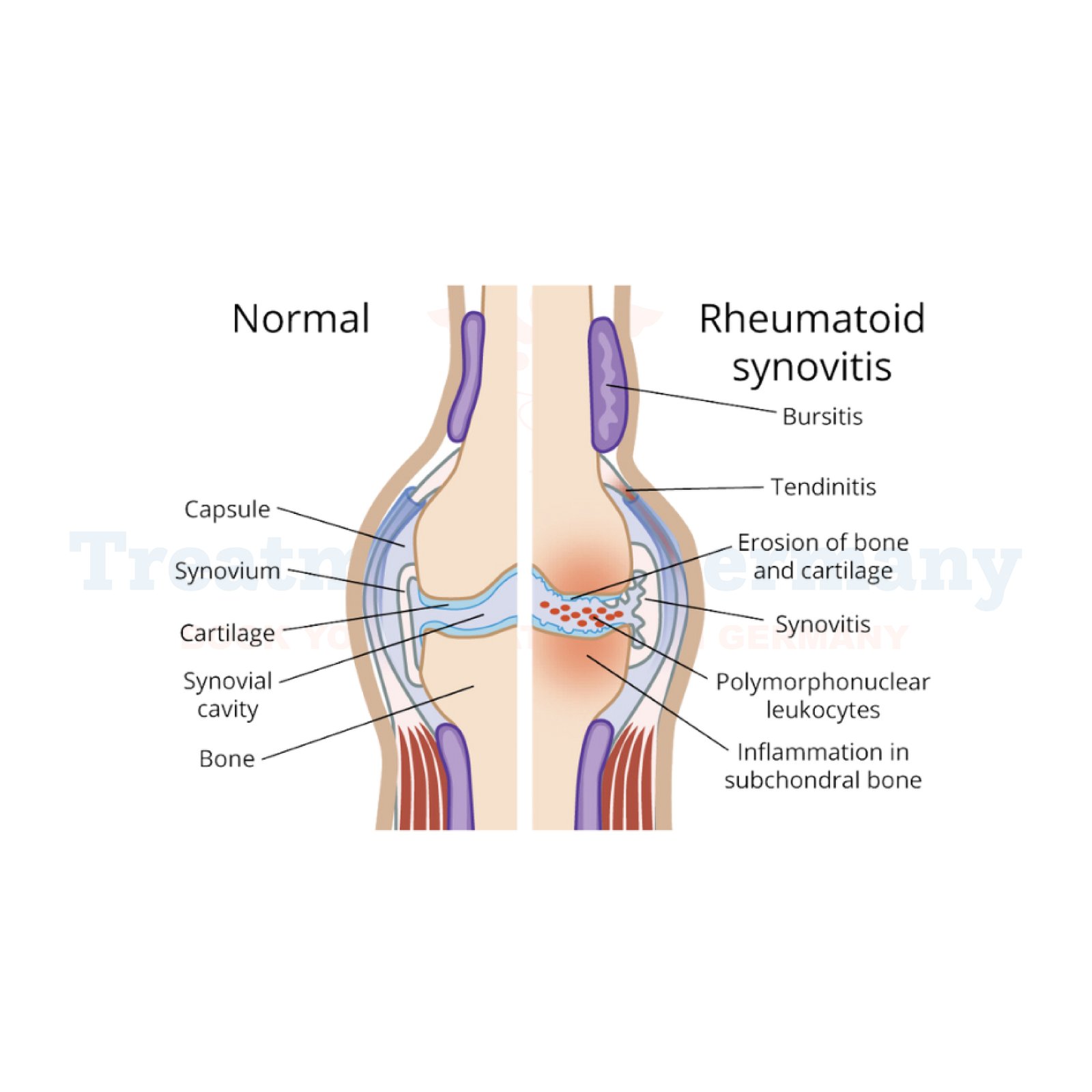
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and potential joint damage. Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear on the joints, RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, particularly the synovium, the lining of the joints. Over time, this leads to joint deformities, reduced mobility, and potentially serious complications.
RA can also affect other organs and systems, including the skin, eyes, lungs, and heart. Although there is no cure for RA, early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent severe damage, making it important to seek expert care.
Types of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is primarily categorized based on the severity and location of the disease:
- Seropositive RA: This type is characterized by the presence of specific antibodies (rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP) in the blood. Seropositive RA typically has a more aggressive course and a higher risk of joint damage.
- Seronegative RA: In this type, rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies are not detectable in the blood, but the disease still causes inflammation and joint damage. It may present with milder symptoms but can still progress to significant joint impairment.
- Juvenile RA: Occurring in children under 16, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis affects the joints and can have an impact on growth and development.
Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Several factors increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis:
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role, as certain genes make individuals more susceptible to autoimmune diseases like RA.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop rheumatoid arthritis, with the condition being 2-3 times more common in females.
- Age: RA typically develops between the ages of 30 and 60, although it can affect people of all ages, including children.
- Smoking: Smoking has been identified as a major environmental risk factor for RA, particularly in those with a genetic predisposition.
- Obesity: Increased body mass index (BMI) can contribute to the onset and progression of RA, as the additional weight puts extra strain on the joints.
- Other autoimmune diseases: Individuals with other autoimmune conditions, such as lupus or thyroid disorders, may have a higher risk of developing RA.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Joint Pain and Swelling: The joints, especially in the hands, wrists, knees, and feet, become painful, swollen, and stiff.
- Morning Stiffness: One of the hallmark symptoms of RA is prolonged stiffness after waking up, which may last for an hour or more.
- Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is common in RA due to the inflammation affecting the body.
- Fever: Some individuals may experience low-grade fevers during flare-ups.
- Loss of Appetite: RA can cause decreased appetite due to the inflammatory response in the body.
- Joint Deformities: Over time, untreated RA can cause permanent joint damage, leading to deformities and impaired function.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, and imaging studies. The tools used to diagnose RA include:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can reveal the presence of specific antibodies (rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP) that are common in RA. Inflammation markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) can also be elevated.
- X-rays: X-ray images can help detect joint damage and inflammation caused by RA, especially in advanced stages.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI scans provide more detailed images of the joints and soft tissues, helping to detect early joint damage and inflammation.
- CT scan (Computed Tomography): CT scans are used less commonly but can offer detailed images of joints and surrounding structures.
- Physical Exam: Doctors will check for signs of joint swelling, tenderness, and deformities. They may also assess the range of motion and functional impairment.
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Germany
Germany is known for its world-class healthcare system, with highly skilled doctors and specialists offering the latest treatments for rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment options in Germany focus on managing symptoms, preventing joint damage, and improving the quality of life. The country’s hospitals are equipped with the latest diagnostic tools and offer a variety of therapies to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Medication Management
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs help reduce inflammation and pain. Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac.
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): DMARDs are the cornerstone of RA treatment, working to slow the disease's progression. Methotrexate is one of the most commonly prescribed DMARDs in Germany, and it may be taken in combination with other medications.
- Biologic DMARDs: In cases of moderate to severe RA, biologic DMARDs, such as TNF inhibitors (adalimumab, etanercept) and IL-6 inhibitors (tocilizumab), are prescribed. These medications target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent joint damage.
- Corticosteroids: Oral or injected corticosteroids like prednisone can provide rapid relief of inflammation but are used sparingly due to potential side effects with long-term use.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist in Germany works with patients to improve joint function, strength, and flexibility. They guide patients in exercises that help reduce stiffness and maintain mobility.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapists help patients adapt to daily tasks, offering tips and tools to ease the stress on inflamed joints.
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact exercises, such as swimming or walking, can help maintain joint function and reduce stiffness without causing additional strain.
Surgical Treatment
In severe cases where medications and physical therapy are not effective, surgery may be required to repair or replace damaged joints. Common surgical procedures include:
- Joint Replacement Surgery: In cases of severe joint destruction, particularly in the hips, knees, or wrists, joint replacement surgery may be recommended to improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Synovectomy: This involves removing the inflamed lining of the joint (synovium) to reduce pain and prevent further joint damage.
- Arthrodesis: In some cases, a joint may be surgically fused to prevent pain and restore function.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Germany offers several complementary therapies that can enhance conventional treatment:
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture is used to relieve pain and inflammation associated with RA, providing patients with an alternative or adjunct to traditional pain management.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and alleviate pain in affected areas.
- Dietary Adjustments: Nutritional counseling may be offered to patients, focusing on reducing inflammation through dietary changes. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help manage symptoms.
Why is it Preferable to Get Treatment in Germany?
Germany is considered one of the leading countries for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, offering several advantages for those seeking care:
- Highly Skilled Doctors and Specialists: German doctors, particularly rheumatologists, are known for their expertise and use of the latest treatment techniques, ensuring that patients receive optimal care.
- Innovative Treatments: Germany is a global leader in medical research, and patients have access to cutting-edge treatments, such as biologic therapies and advanced surgical techniques.
- Comprehensive Care: German hospitals provide holistic, multidisciplinary care, combining medical treatment, physical therapy, and complementary therapies to offer the best chance for symptom relief and long-term management.
- State-of-the-Art Facilities: German healthcare facilities are equipped with the latest diagnostic and treatment technologies, including MRI, CT scans, and advanced imaging techniques that allow for precise diagnosis and monitoring of disease progression.
- Clinical Trials: Patients in Germany have access to clinical trials, which offer the opportunity to participate in studies testing new therapies and drugs for RA.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a challenging autoimmune disease, but with the right treatment, patients can manage symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. Germany’s world-class healthcare system provides innovative and comprehensive treatment options for RA, from medications and physical therapy to advanced surgical procedures.
Whether through biologic therapies, physical rehabilitation, or complementary treatments, patients in Germany can expect personalized care and the latest advancements in the fight against rheumatoid arthritis. Choosing to undergo treatment in Germany means access to leading doctors, hospitals, and cutting-edge therapies that ensure the best outcomes for patients with RA.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
