What is Rickets?
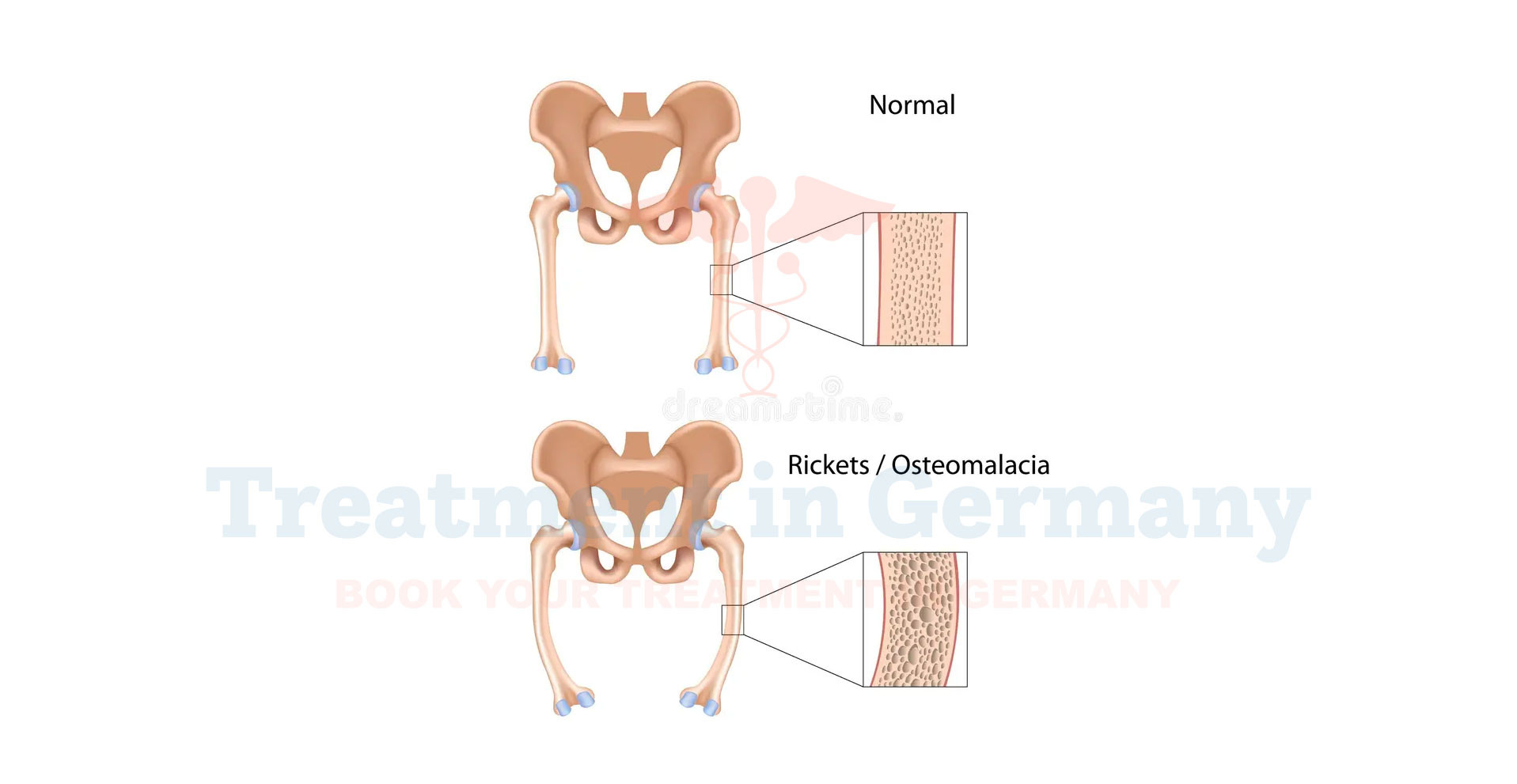
Rickets is a rare but serious condition that primarily affects children, causing weak or soft bones. It occurs due to a deficiency in vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate, crucial nutrients for bone health.
These deficiencies can impair the mineralization process of bones, leading to skeletal deformities and other complications if left untreated.
Side Effects of Rickets
The effects of rickets can manifest in various ways:
- Bone Deformities: Legs that bow outwards or are shaped abnormally, or a prominent forehead and rib cage.
- Delayed Growth: Children may not grow as expected or may have delayed tooth development.
- Muscle Weakness: Weak muscles can contribute to difficulty in walking or motor function.
- Pain: Bone pain, particularly in the spine, pelvis, and legs, can be present.
How is Rickets Diagnosed?
Diagnosing rickets typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests:
- Physical Examination: A doctor may observe physical signs such as bowed legs or knock knees.
- Blood Tests: These can measure levels of vitamin D, calcium, phosphate, and alkaline phosphatase.
- Bone X-rays: X-rays can reveal changes in bone density and structure characteristic of rickets.
Potential Treatment of Rickets
The treatment approach for rickets focuses on addressing the underlying cause and restoring bone health:
- Vitamin D and Calcium Supplements: Correcting deficiencies through prescribed supplements is a primary intervention.
- Sunlight Exposure: Moderate exposure to sunlight can help the body produce vitamin D naturally.
- Dietary Changes: Ensuring a diet rich in vitamin D and calcium, including fortified foods and dairy products.
- Orthopedic Management: In severe cases, orthopedic interventions may be necessary to correct bone deformities.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
