What is Scheuermann's Disease?
Scheuermann's Disease, also known as Scheuermann's kyphosis, is a condition that primarily affects the thoracic spine (upper and middle back) during adolescence.
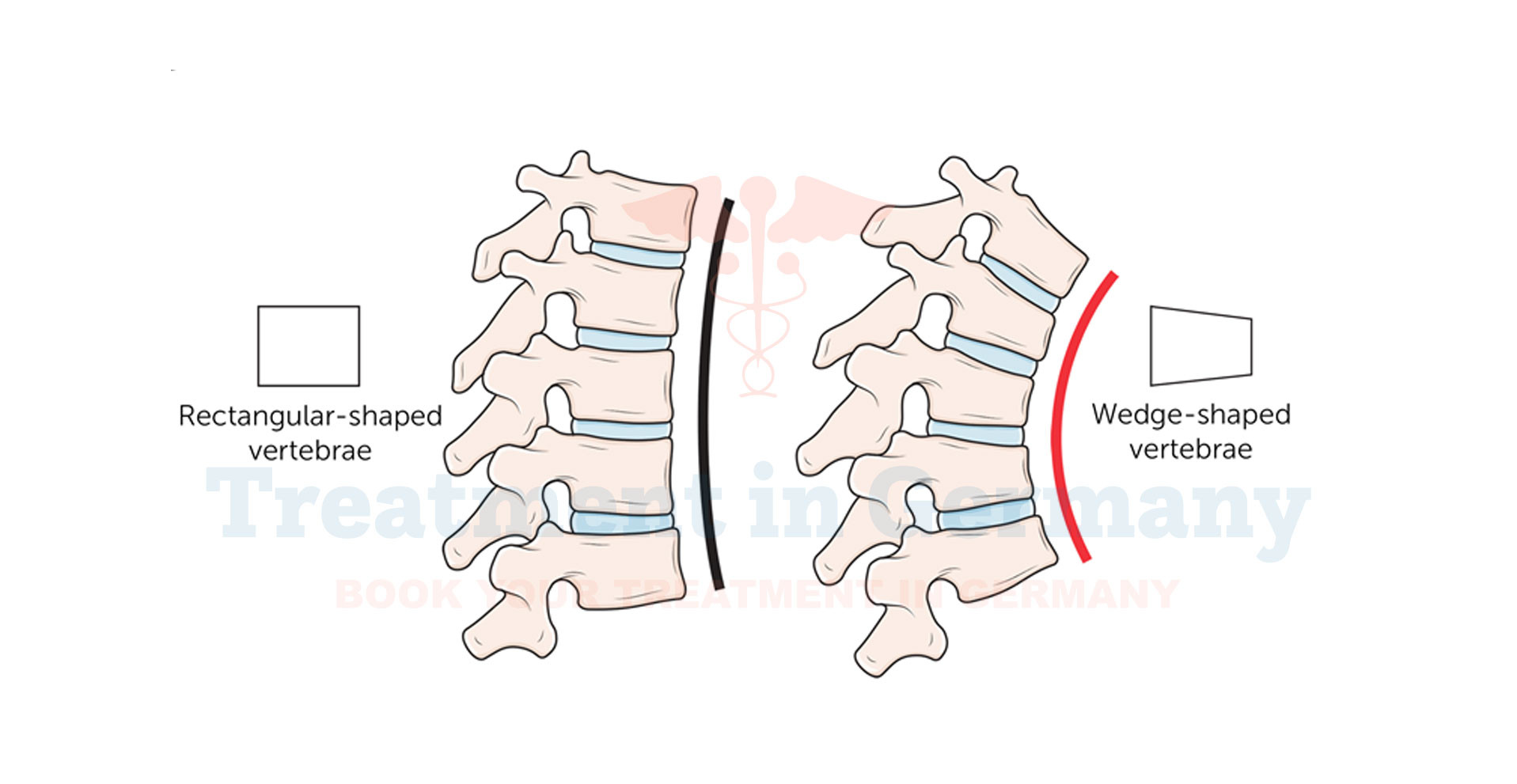
It is characterized by abnormal growth of the vertebrae, leading to a wedging shape instead of the normal rectangular shape. This abnormality causes the spine to curve forward more than usual, resulting in a rounded or hunched back appearance.
Side Effects of Scheuermann's Disease
The main symptoms of Scheuermann's Disease include:
- Back pain: Patients may experience persistent or intermittent pain in the middle or upper back.
- Posture changes: The condition often leads to a noticeable rounding of the upper back (increased thoracic kyphosis) and sometimes a slight forward protrusion of the abdomen.
- Stiffness: The spine may become less flexible over time.
- Fatigue: Some individuals may feel tiredness due to the strain on their back muscles from trying to maintain a normal posture.
How is Scheuermann's Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Scheuermann's Disease typically involves:
- Physical examination: Your doctor will assess your posture, spinal alignment, and range of motion.
- X-rays: These are crucial for confirming the diagnosis by revealing the characteristic wedging of the vertebrae and the degree of spinal curvature.
- MRI or CT scans: These imaging tests may be used to assess the condition of discs and nerves if there are signs of nerve compression or severe pain.
Potential Treatments for Scheuermann's Disease
Treatment options for Scheuermann's Disease depend on the severity of symptoms and the degree of spinal curvature. They may include:
- Observation and monitoring: In mild cases where symptoms are minimal, regular check-ups and monitoring of spinal curvature may be sufficient.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen back muscles and improve posture can help manage pain and prevent further curvature progression.
- Bracing: For adolescents with significant spinal curvature, wearing a brace may be recommended to support the spine and prevent it from worsening during growth spurts.
- Pain management: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other pain relievers may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative measures fail or the curvature is severe and progressive, spinal fusion surgery may be considered to correct the deformity and stabilize the spine.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
