Germany provides state of the art medical treatment, and the treatment of testicular cancer is among them. Though rare, testicular cancer can be treated quite effectively with the best possible results, especially when hospitals in Germany are equipped with the latest techniques and specialized care.
The Germany’s Health System offers innovative treatment and a profoundly deep cure so that patients receive results with the highest possible outcome.
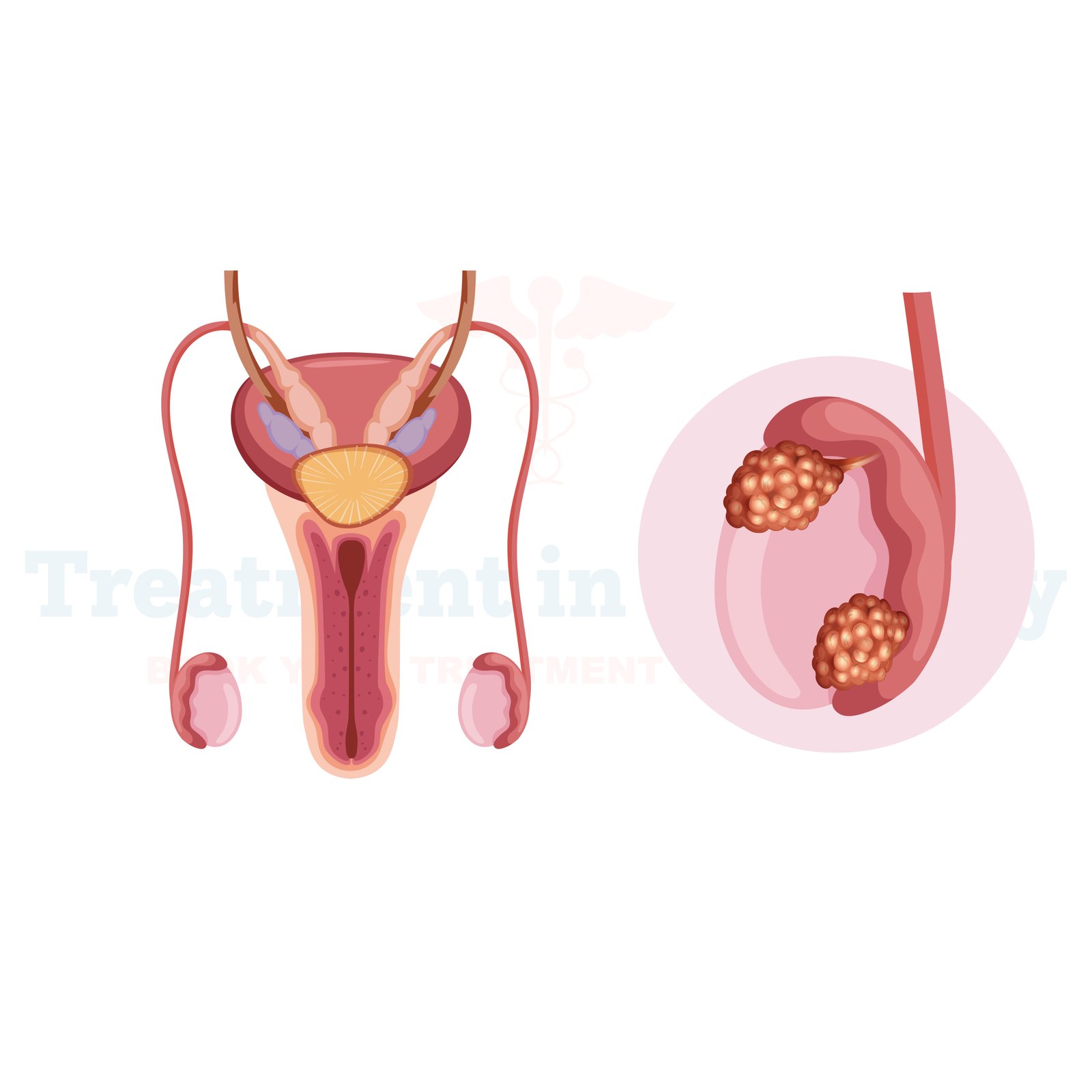
Testicular cancer is the uncontrolled multiplication of abnormal cells within the testicles. The organs in charge of producing sperm and testosterone are called testicles, or sex glands. Although testicular cancer is a rare form of cancer, most cases occur in men in the range of 15 to 35 years old. Thus, timely diagnosis is significant for a successful treatment.
Based on the detection process, medical diagnosis most times relies on check ups and medical images.
Classification of Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer is divided into two major
categories:
German clinics treat both of these types using different surgical methods for the testicular cancer as well as different therapies.
Diagnosis of Testicular Cancer in Germany
German healthcare organizations are developed highly for making proper diagnostics for testicular cancer. The diagnostic process usually begins with a physical examination of lumps or abnormalities found in the testicles.
Early Detection of Testicular Cancer
German tests include:
The primary outcome of treatment depends upon
early detection. In Germany, these diagnostic tests are as follows:
These tests would be useful in determining the stage of the cancer. Cancer staging would help the doctors devise a treatment plan.
Testicular Cancer Treatment Centers in Germany
The hospitals in Germany have mastered the science of precision, expertise, and the latest state of the art technologies. Most major clinics are well equipped with the latest diagnostic tools and treatment procedures. Some hospitals also provideinnovative testicular cancer treatments.
Innovative Testicular Cancer Treatments
Germany offers a wide range of treatments that
include:
Many hospitals in Germany also become involved with other German hospitals that specialize in testicular cancer techniques to advance positive outcomes in patients.
Dendritic Cell Therapy
Dendritic cell therapy is an advanced form of immunotherapy that enhances the body’s immune system to target and destroy testicular cancer cells.
Hyperthermia Therapy
Hyperthermia therapy is used as a complementary treatment for testicular cancer, often combined with chemotherapy or radiation to boost their effectiveness.
High-Dose Chemotherapy with Stem Cell Support
For advanced or recurrent testicular cancer, high-dose chemotherapy combined with stem cell transplantation is a powerful treatment option.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific genetic mutations or proteins in cancer cells, offering a more personalized approach to treatment.
Psychological Counseling
If nothing else, the fight against cancer means facing several psychological challenges. Some hospitals provide counseling for the psychological stress that cancer and its treatment invoke.
Treatment Cost of Testicular Cancer in Germany
The cost of testicular cancer treatment in Germany is determined by type and stage, as well as the specific hospital. Germany presents cutting edge and notably priced treatments, offering world-class care at competitive prices. Many hospitals offer packages of diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation services.
Best Testicular Cancer Treatment Hospitals in Germany
Germany has numerous top ranked hospitals that
specialize in testicular cancer surgery options and therapies:
These clinics are famous for their high success rates and the use of advanced technologies.
Benefits to treat it in Germany
There are many benefits to receiving medical care in Germany:
Super Advantages of Treatment in Germany
Management Interventions of Testicular Cancer in Germany
Testicular cancer is primarily treated with surgery, including orchiectomy, and also chemotherapy and radiation therapy when necessary, depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Through which methods is testicular cancer diagnosed in Germany?
Doctors conduct several tests including physical exams, ultrasounds, CT scans, and X-rays, to identify testicular cancer as well as stage, appropriately to offer the correct treatment planning.
What are the reasons why Germany is at the top level in testicular cancer treatment?
Germany provides state of the art medical technology and highly experienced professionals, along with innovative treatments, which combined give the greatest success while treating testicular cancer.
How much does testicular cancer treatment cost in Germany?
The hospital and form of treatment differ in cost, but German hospitals charge competitively for the best, most comprehensive cancer care in the world.
In Germany, are there services for rehabilitation accessible following treatment for testicular cancer?
Yes, in Germany, there are hospitals, that can
provide for rehabilitation specifically targeted to support the patient's
physical and mental recovery.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
