Understanding Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
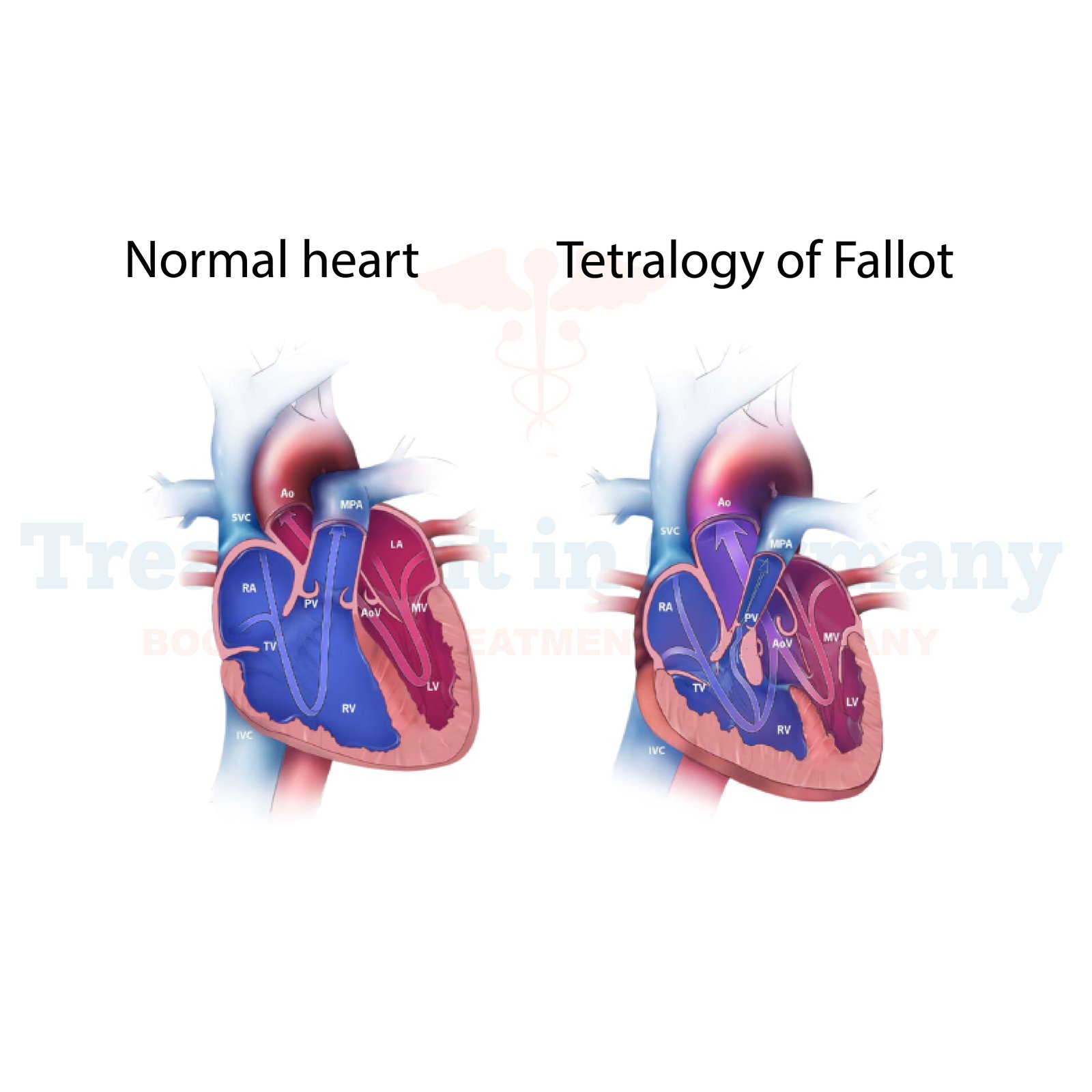
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect that affects the structure of the heart, leading to a variety of symptoms and challenges.
It is one of the most common congenital heart defects, occurring in about 3 out of every 10,000 live births.
Side Effects of Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
TOF involves four main heart defects:
These defects can lead to a range of symptoms, including cyanosis (blue tint to the skin due to lack of oxygen), shortness of breath, rapid breathing, fainting spells, and difficulty feeding or growing in infants.
Diagnosis of Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Tetralogy of Fallot is typically diagnosed soon after birth or during infancy. Diagnosis often involves:
Potential Treatment of Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Treatment of Tetralogy of Fallot usually involves surgical intervention to correct the heart defects. The timing and type of surgery depend on the severity of the condition and the child's overall health. Common procedures include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
