Treatment for vulvar cancer is offered by Germany as one of the best places in the world, where the most recent and advanced medical solutions are available, customized to fit the needs of each patient.
Vulvar cancer is a rare malignancy developing in the external sex organs, often because of abnormal cell growth. This article delves into the illness, its causes, symptoms, and the cutting edge treatments that are accessible in Germany.
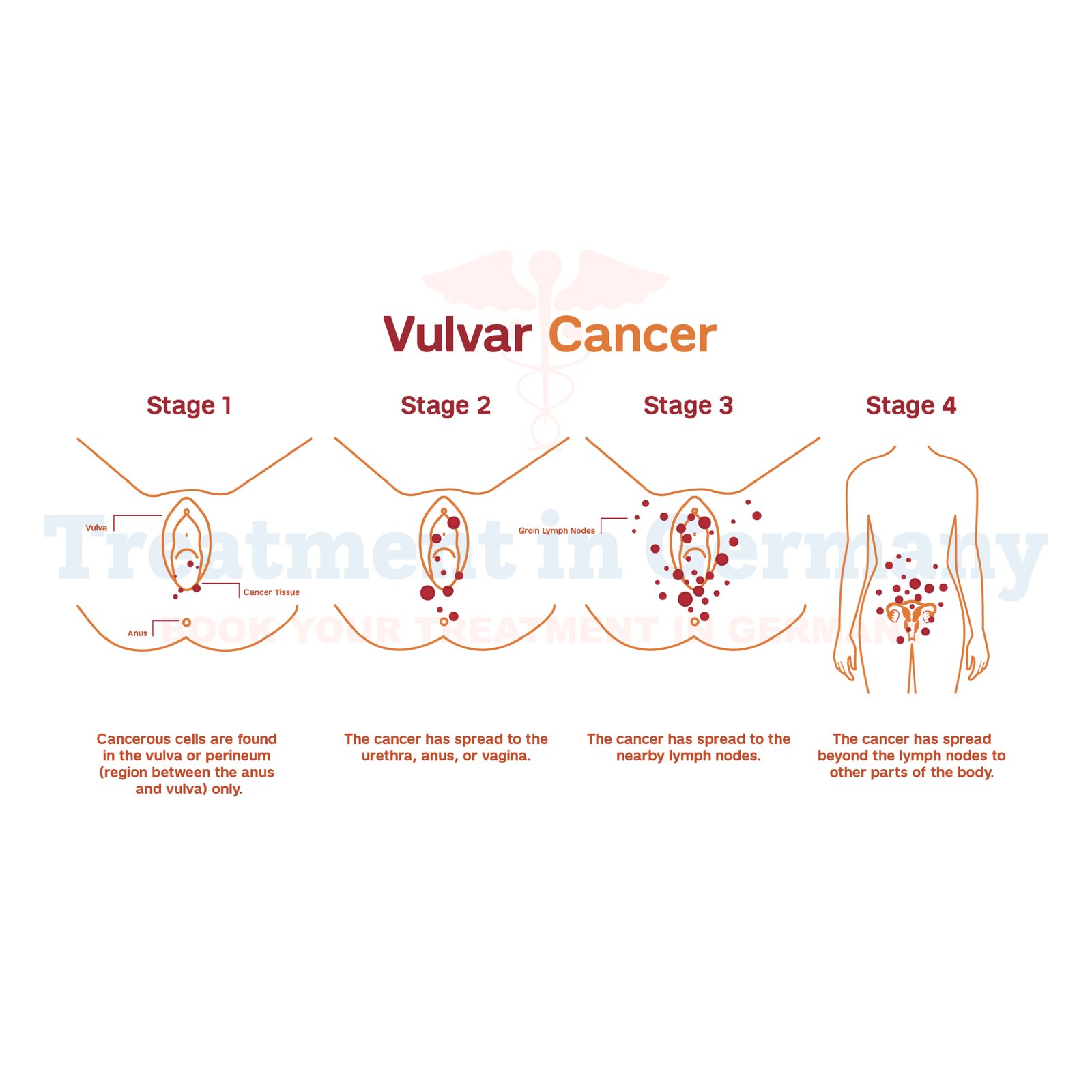
Vulvar cancer is a form of cancer that starts in the outer portion of the female genitalia, often referred to as the vulva. The vulva consists of the labia, clitoris, urethra, and perineum.
Abnormal cells often begin as skin lesions that may develop into malignant tumors. It is a cancer typically diagnosed in older women. Most cases occur in women over 65 years, but vulvar cancer can occur at any age.
Types of Vulvar Cancer
The classification of vulvar cancer is based on the origin of the malignancy in the cells:
Vulvar cancer is typically slow in progression. However, if diagnosed early, it can possibly be treated.
Causes and Risk Factors of Vulvar Cancer
Causes
The development of vulvar cancer begins with the cells of the vulva carrying mutated DNA, which causes them to multiply uncontrollably. After several years, these damaged cells invade surrounding tissues and metastasize to lymph nodes or other parts of the body, such as the bladder and anus.
Risk Factors
The following factors could increase the likelihood that someone may get vulvar cancer:
These risk factors will allow individuals and healthcare professionals to know which complications might or might not have an effect.
Symptoms of Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar cancer symptoms are nonspecific until the disease is well advanced but can include the following:
The above symptoms must be treated with immediate medical attention. Stage one cancer provides a higher possibility of treatment being adequately successful.
Diagnosis of Vulvar Cancer in Germany
In Germany, advanced methods are utilized within its healthcare system to ensure the proper diagnosis of vulvar cancer.
Diagnostic Process
These advanced diagnostic tools provide proper evaluation, hence accurate staging and proper treatment planning.
Vulvar Cancer Treatment Methods in Germany
German health centers offer various state-of-the-art and customized treatments for vulvar cancer.
Surgical Interventions
Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation therapy is the most common type used to shrink tumors before surgery or destroy remaining cancer cells after surgery.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is administered either intravenously or topically as a cream for localized lesions. It is administered with radiation for best outcomes.
Immunotherapy
The drugs like Imiquimod are given to enhance the body's ability to detect and destroy cancerous cells.
Multidisciplinary Treatment of Complications
All the conditions that may arise during the course of vulvar cancer treatment. German doctors generally treat, with an integrated approach, multiple risk symptoms and conditions, including:
Diabetes, shortness of breath, dizziness, and chest pain are also controlled in the treatment process to ensure a holistic recovery for the patdetects
Prevention and Prognosis
Prevention Measures
Prognosis
Proper treatment is ensured with early diagnosis. The five-year survival rate for localized vulvar cancer is more than 85%, but this dramatically falls when cancer starts spreading around different parts of the body.
Germany does have advanced imaging technology like cerebral angiograms, ensuring proper detection with high accuracy rates of the treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the significant symptoms and signs of vulvar cancer?
The most common symptoms are itches persisting for a long time, skin discoloration, and ulcers or lumps in the vulva.
How is vulvar cancer treated in Germany?
Treatment modalities include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy to which the patient will be subjected depending on the type of cancer diagnosis.
Can other diseases also be kept under check during cancer treatment?
Yes, most of the hospitals in Germany treat stroke, diabetes, and shortness of breath along with cancer treatment.
What are the risk factors for vulvar cancer?
HPV infection, lichen sclerosis-chronic skin conditions, smoking, and weak immunity are considered to be major risk factors.
How to reduce the risk of vulvar cancer?
Get vaccinated against HPV, quit smoking, and come regularly to a gynecological visit to check for abnormal cells.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
