What is Acromegaly:
Acromegaly is a rare hormonal disorder characterized by the excessive production of growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) in the body.
This overproduction usually stems from a benign tumor in the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. These elevated levels of growth hormone and IGF-1 can lead to a variety of physical changes and health complications.
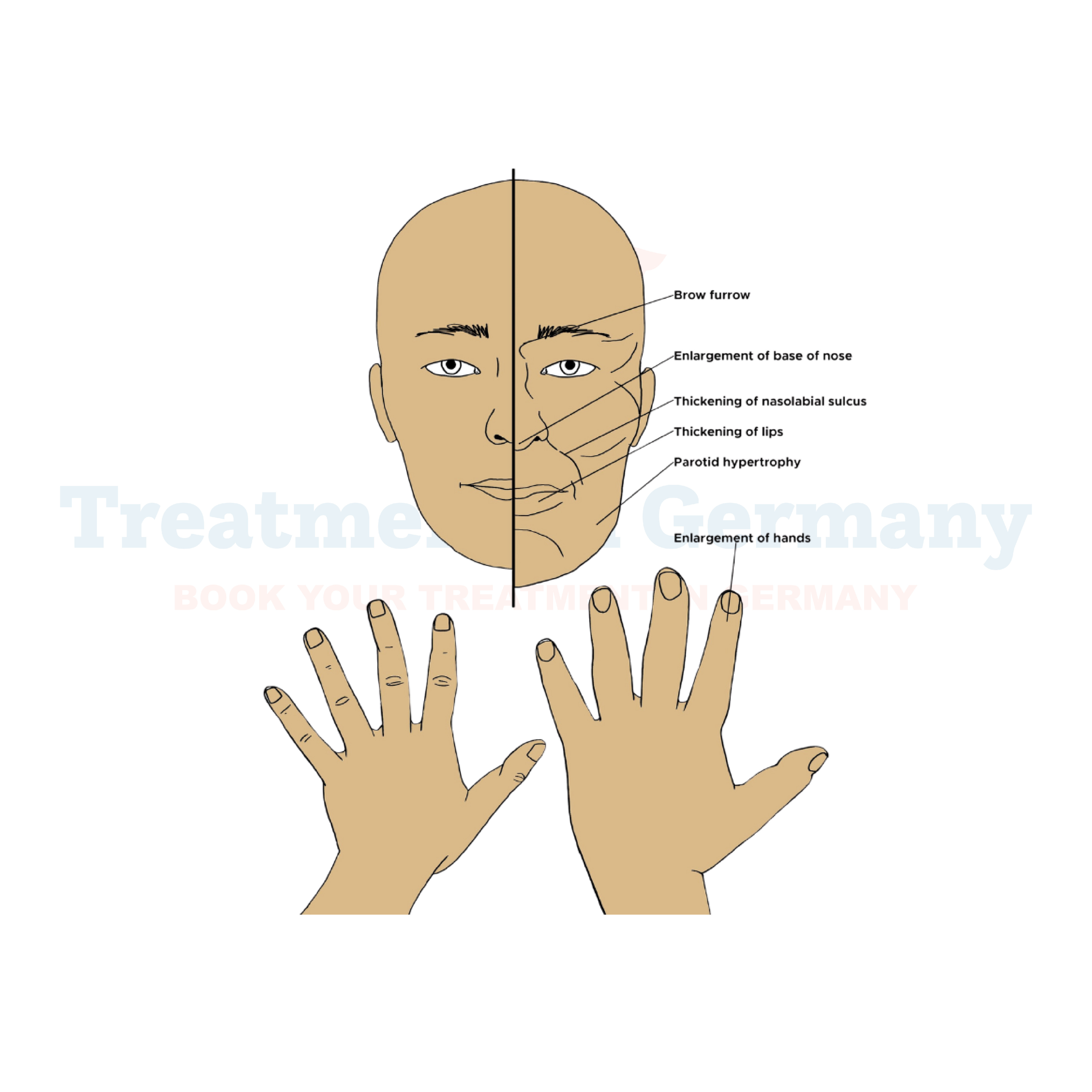
Side effects of Acromegaly:
The symptoms of acromegaly often develop gradually and can vary from person to person. Common signs and side effects include:
How is Acromegaly diagnosed?
Diagnosing Acromegaly typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Key diagnostic steps may include:
1. Hormone testing: Blood tests to measure levels of growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) can help confirm the diagnosis.
2. Imaging studies: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans of the brain are often used to locate and assess the size of the pituitary tumor.
3. Visual field testing: If the tumor is pressing on the optic nerves, visual field testing may be conducted to evaluate any vision changes.
Potential treatments of Acromegaly:
Treatment for acromegaly aims to reduce the production of excess growth hormone, alleviate symptoms, and minimize complications. Options may include:
1. Surgery: Transsphenoidal surgery, a minimally invasive procedure to remove the pituitary tumor, is often the first-line treatment for Acromegaly.
2. Medications: If surgery is not successful or feasible, medications such as somatostatin analogs, dopamine agonists, and growth hormone receptor antagonists may be prescribed to lower GH and IGF-1 levels.
3. Radiation therapy: In cases where surgery and medications are ineffective, radiation therapy may be used to shrink or control the growth of the pituitary tumor.
4. Follow-up care: Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to assess treatment effectiveness, manage symptoms, and monitor for potential complications.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
