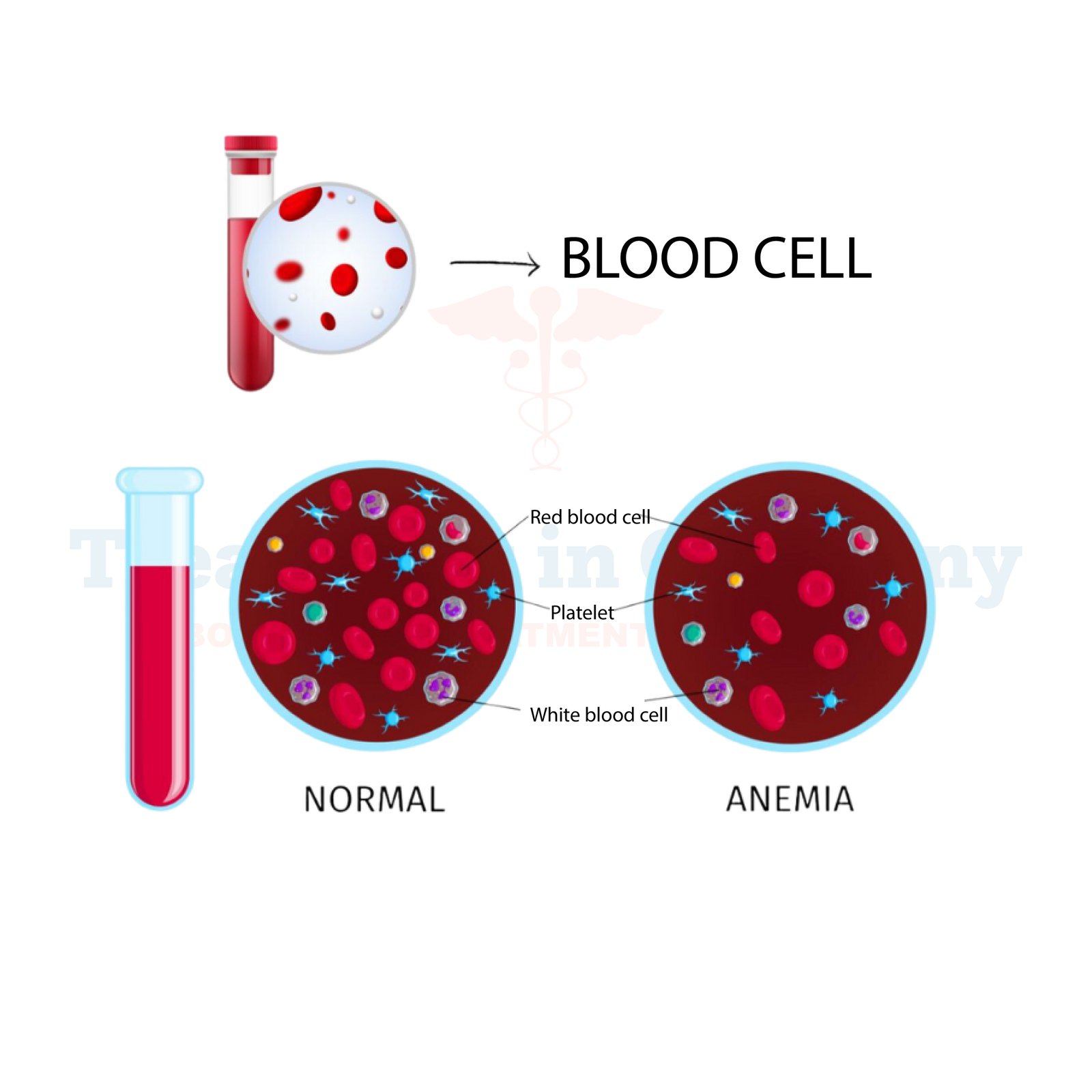
What is Anemia:
Anemia is a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood. Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body, and hemoglobin is the protein in these cells that binds oxygen. When there's a shortage of either, the body doesn't get enough oxygen, leading to a range of symptoms and potential health complications.
Side effects of Anemia:
The symptoms of anemia can vary depending on its severity and underlying cause. Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pale or yellowish skin, shortness of breath, dizziness or lightheadedness, cold hands and feet, irregular heartbeat, headache, and chest pain. Severe anemia may lead to complications such as heart problems, pregnancy complications, and impaired cognitive function.
How is Anemia diagnosed?
Diagnosing anemia typically involves a series of blood tests to measure various components of the blood, including red blood cell count, hemoglobin levels, hematocrit (the proportion of red blood cells in the blood), and mean corpuscular volume (the size of red blood cells). Additional tests may be performed to determine the underlying cause of the anemia, such as iron deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, or chronic diseases.
Potential treatments of Anemia:
The treatment of anemia depends on its underlying cause and severity. Common treatments include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
