What is Diabetic Nephropathy?
Diabetic Nephropathy is a serious complication of diabetes that affects the kidneys. When diabetes is not well managed, high levels of sugar in the blood can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney damage and ultimately, kidney failure. Diabetic Nephropathy is one of the leading causes of end-stage kidney disease worldwide.
Side effects of Diabetic Nephropathy
Left untreated or poorly managed, Diabetic Nephropathy can lead to a range of serious health complications. These may include high blood pressure, fluid retention, electrolyte imbalances, anemia, bone disease, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Moreover, as kidney function declines, waste products and toxins can build up in the body, leading to symptoms like fatigue, swelling in the legs, nausea, vomiting, itching, and shortness of breath.
How is Diabetic Nephropathy diagnosed?
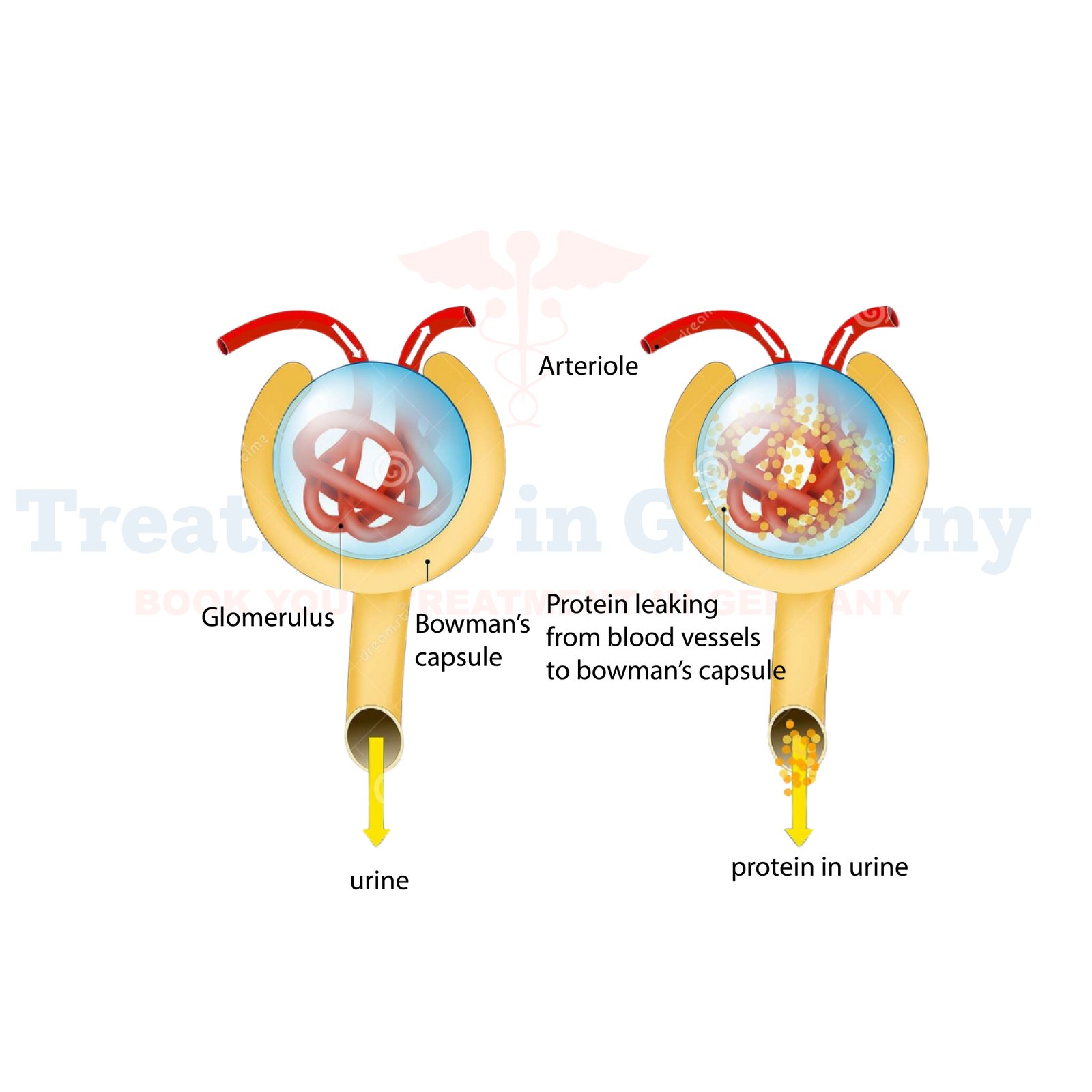
Diagnosing Diabetic Nephropathy typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Your doctor may conduct urine tests to check for the presence of protein (proteinuria), which is a hallmark sign of kidney damage. Blood tests may also be performed to assess kidney function by measuring creatinine levels and estimating the glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Additionally, imaging studies such as ultrasound or kidney biopsy may be recommended to evaluate the extent of kidney damage.
Potential treatments of Diabetic Nephropathy
The management of Diabetic Nephropathy aims to slow down the progression of kidney damage, control symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment strategies often include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
