What is Distal Urethral Stenosis
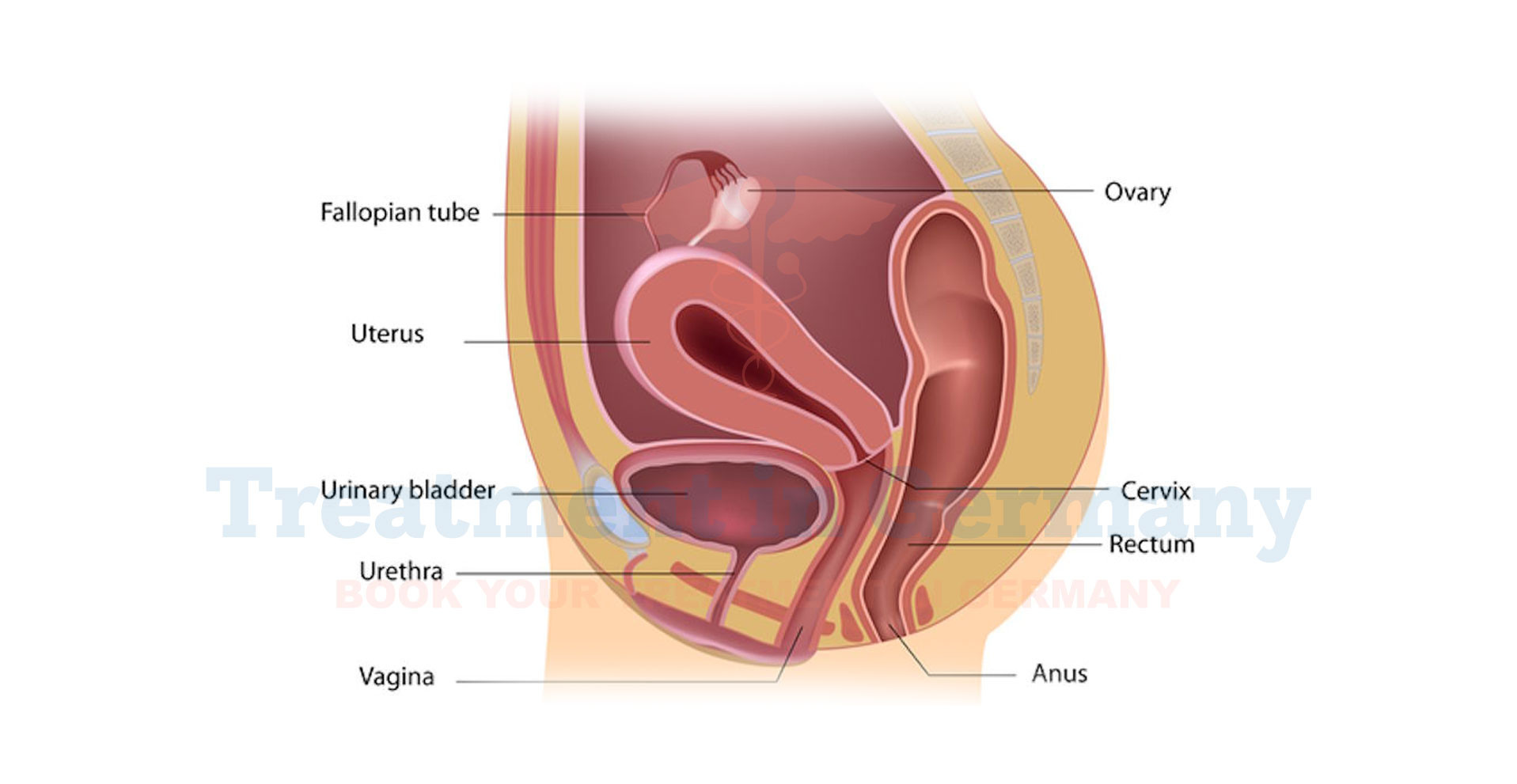
Distal urethral stenosis is a condition characterized by a narrowing of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
This narrowing occurs specifically at the distal end of the urethra, which is the portion closer to the external opening. This condition can lead to various urinary problems, including difficulty urinating and increased risk of infections.
Side Effects of Distal Urethral Stenosis
The narrowing of the urethra can result in several symptoms and complications, including:
- Difficulty Urinating: Patients may experience a weak urine stream or trouble starting and maintaining urination.
- Painful Urination: Discomfort or pain during urination can occur due to the increased pressure required to push urine through the narrowed area.
- Frequent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): The narrowing can make it harder to fully empty the bladder, leading to an increased risk of infections.
- Bladder Irritation: Chronic irritation or inflammation of the bladder can result from prolonged obstruction.
- Urinary Retention: In severe cases, the inability to pass urine properly can lead to urinary retention, which may require immediate medical attention.
How is Distal Urethral Stenosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of distal urethral stenosis involves several steps:
- Medical History and Symptom Review: Your healthcare provider will start by asking about your symptoms, medical history, and any past urinary issues.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may be conducted to assess symptoms and check for any visible abnormalities.
- Urodynamic Testing: This test measures how well the bladder and urethra are functioning. It helps determine the degree of obstruction and its impact on urination.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound or other imaging techniques may be used to visualize the urethra and bladder, identifying areas of narrowing or obstruction.
- Cystoscopy: This procedure involves inserting a thin tube with a camera (cystoscope) into the urethra to directly observe the inside of the urethra and bladder. It helps in precisely locating the stenosis and assessing its severity.
Potential Treatment of Distal Urethral Stenosis
Treatment options for distal urethral stenosis vary based on the severity of the condition and the patient's overall health. Common approaches include:
- Urethral Dilation: This procedure involves using a balloon or other instruments to gently stretch the narrowed area of the urethra, improving urine flow.
- Urethrotomy: A surgical procedure where a small incision is made in the narrowed part of the urethra to widen it and relieve the obstruction.
- Surgical Reconstruction: For more severe or recurrent cases, surgical reconstruction of the urethra may be necessary to remove the stenotic segment and restore normal function.
- Medications: Although not a primary treatment, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms or prevent infections associated with the condition.
- Lifestyle and Behavioral Changes: In some cases, adjusting fluid intake, urinary habits, and avoiding irritants can help manage symptoms and prevent further complications.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
