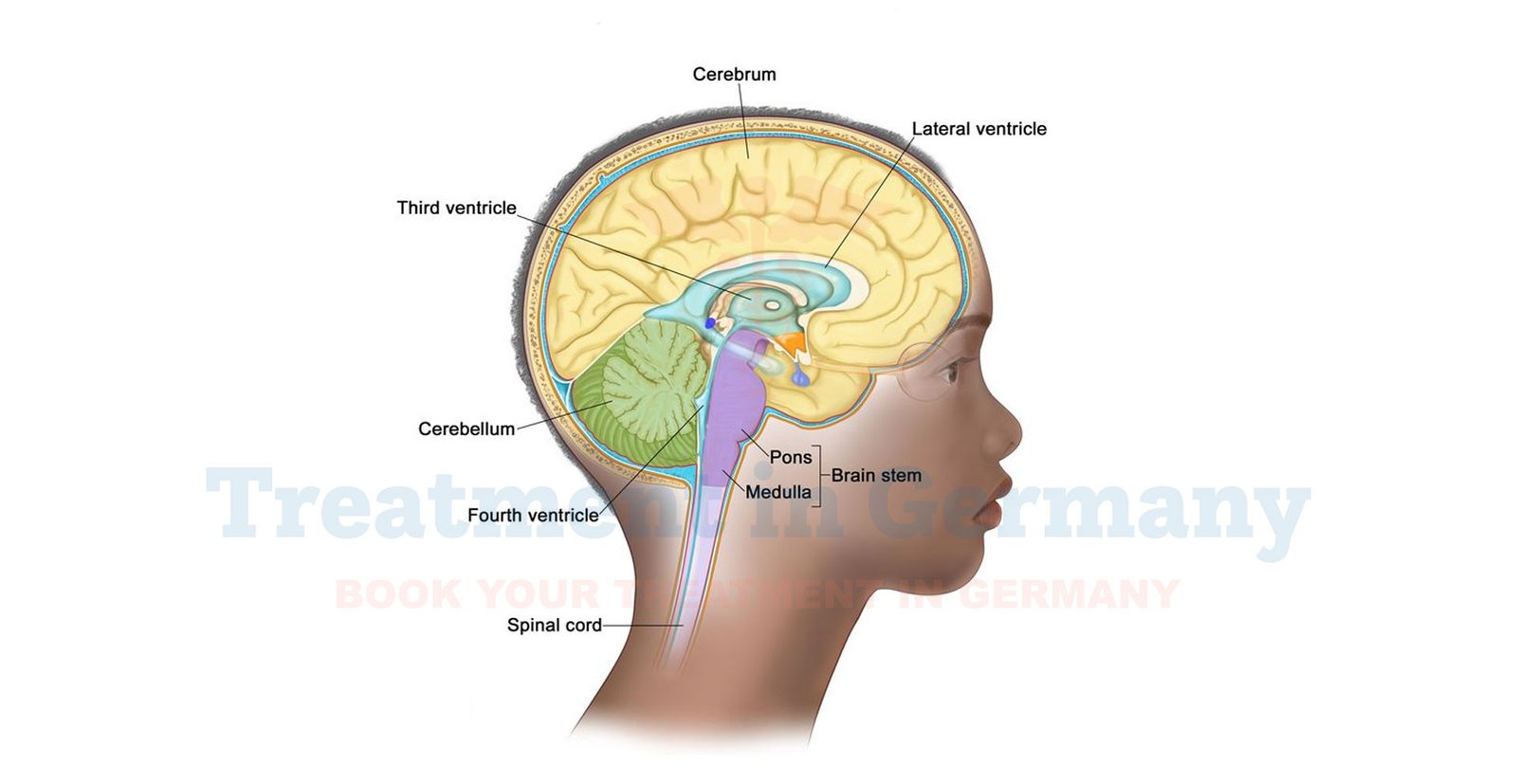
What is Ependymoma?
Ependymoma is a type of tumor that originates in the cells lining the fluid-filled spaces in the brain and spinal cord.
These tumors are relatively rare and can occur at any age, but they most commonly affect children and young adults.
The exact cause of ependymomas is not well understood, but genetic factors and mutations may play a role in their development.
Side Effects of Ependymoma
The symptoms and side effects of ependymoma can vary depending on the location and size of the tumor. Common symptoms may include:
- Headaches: Persistent or worsening headaches, especially in the morning.
- Nausea and vomiting: Often accompanied by headaches.
- Changes in vision or balance: Due to pressure on the brain or spinal cord.
- Seizures: Especially if the tumor affects areas of the brain responsible for controlling seizures.
- Motor or sensory deficits: Weakness, numbness, or difficulty with coordination.
The specific symptoms experienced can help doctors determine the location of the tumor and its impact on surrounding tissues.
How is Ependymoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosing ependymoma typically involves a combination of imaging tests and biopsy:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This imaging technique helps visualize the location, size, and characteristics of the tumor.
- CT scan (Computed Tomography): Sometimes used to provide additional information about the tumor.
- Biopsy: A sample of the tumor tissue is collected and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis and determine the grade of the tumor (how quickly it is likely to grow).
Potential Treatment of Ependymoma
Treatment for ependymoma depends on several factors, including the location, size, and grade of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. Common treatment options may include:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for ependymoma is surgical removal of as much of the tumor as possible without causing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Radiation Therapy: Often used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence, especially for higher-grade tumors.
- Chemotherapy: Sometimes used, particularly in young children or when the tumor cannot be completely removed surgically.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
