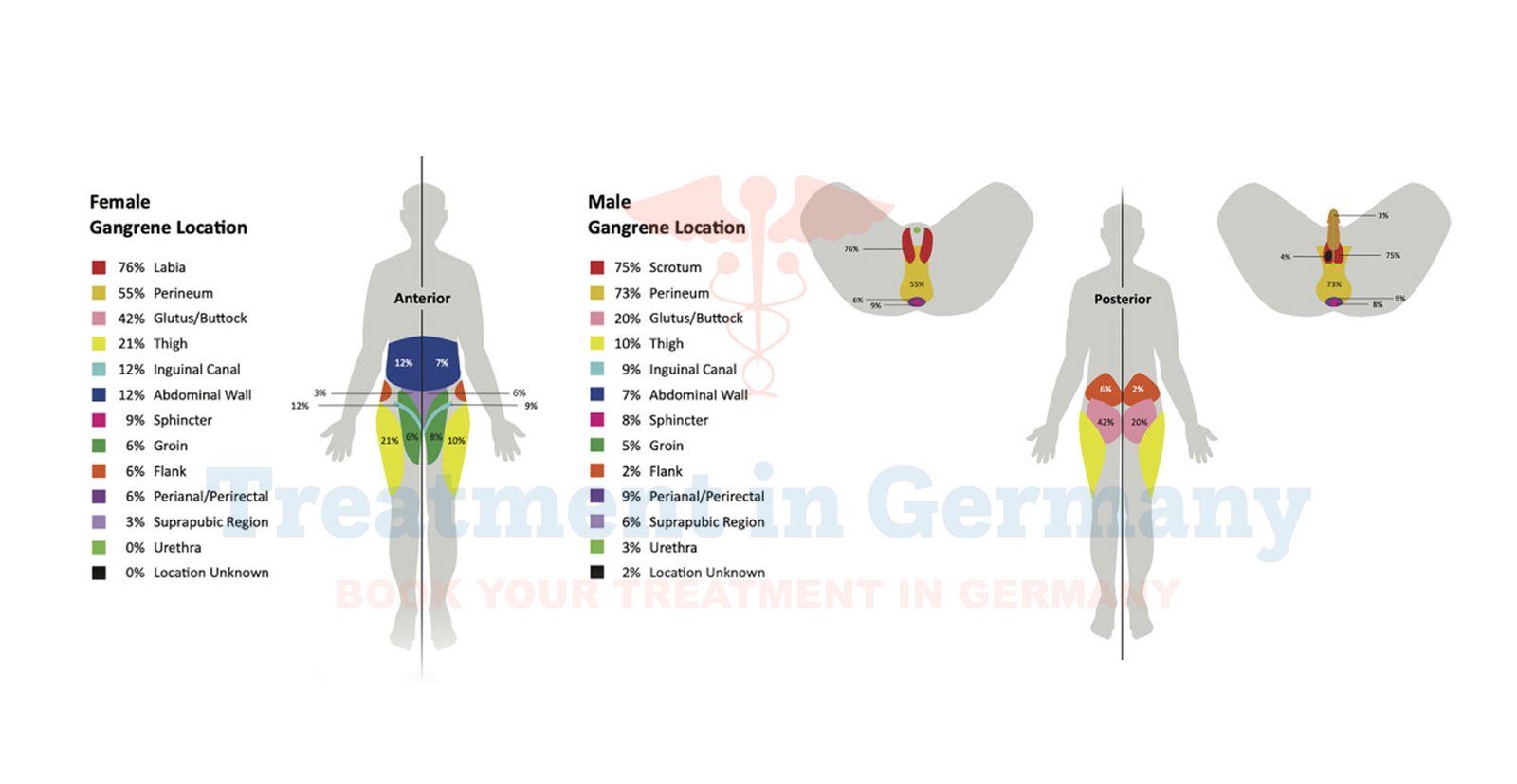
What is Fournier's Gangrene?
Fournier's gangrene is a rare but serious condition characterized by a rapidly progressing infection of the soft tissues in the genital and perineal areas.
This condition, named after the French surgeon Jean-Alfred Fournier who first described it in the 19th century, involves the necrosis (tissue death) of these regions due to a polymicrobial infection, which includes a mix of bacteria, fungi, and sometimes viruses.
The infection usually starts in the skin or mucous membranes and can quickly spread to deeper tissues.
Side Effects of Fournier's Gangrene
The side effects of Fournier's gangrene are severe and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Common symptoms and complications include:
- Severe pain and swelling in the genital or perineal area.
- Fever and chills indicating a systemic response to the infection.
- Rapidly spreading skin discoloration and necrosis (blackening) of the affected area.
- Sepsis, a serious bloodstream infection that can lead to shock and organ failure.
- Loss of function in the affected area due to tissue damage.
How is Fournier's Gangrene Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Fournier's gangrene involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests:
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the affected area to assess the extent of tissue damage and infection.
- Blood Tests: To identify markers of infection, inflammation, and organ function.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may be used to visualize the extent of the infection and tissue damage.
- Microbiological Cultures: Samples from the infected tissue may be cultured to identify the specific bacteria or fungi causing the infection.
Potential Treatment of Fournier's Gangrene
Prompt and aggressive treatment is crucial for managing Fournier's gangrene. Treatment typically involves:
- Surgical Intervention: Immediate surgical debridement (removal of necrotic tissue) is essential to control the infection and prevent its spread. Multiple surgeries may be needed.
- Antibiotics: Broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics are administered to target the wide range of bacteria involved. Once specific pathogens are identified, antibiotic therapy may be adjusted.
- Supportive Care: This includes managing fluid balance, blood pressure, and other vital signs to support overall health and recovery.
- Wound Care: Advanced wound care techniques may be employed to facilitate healing and minimize complications.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: In some cases, this therapy may be used to enhance tissue oxygenation and aid in the healing process.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
