What is Glomerulonephritis?
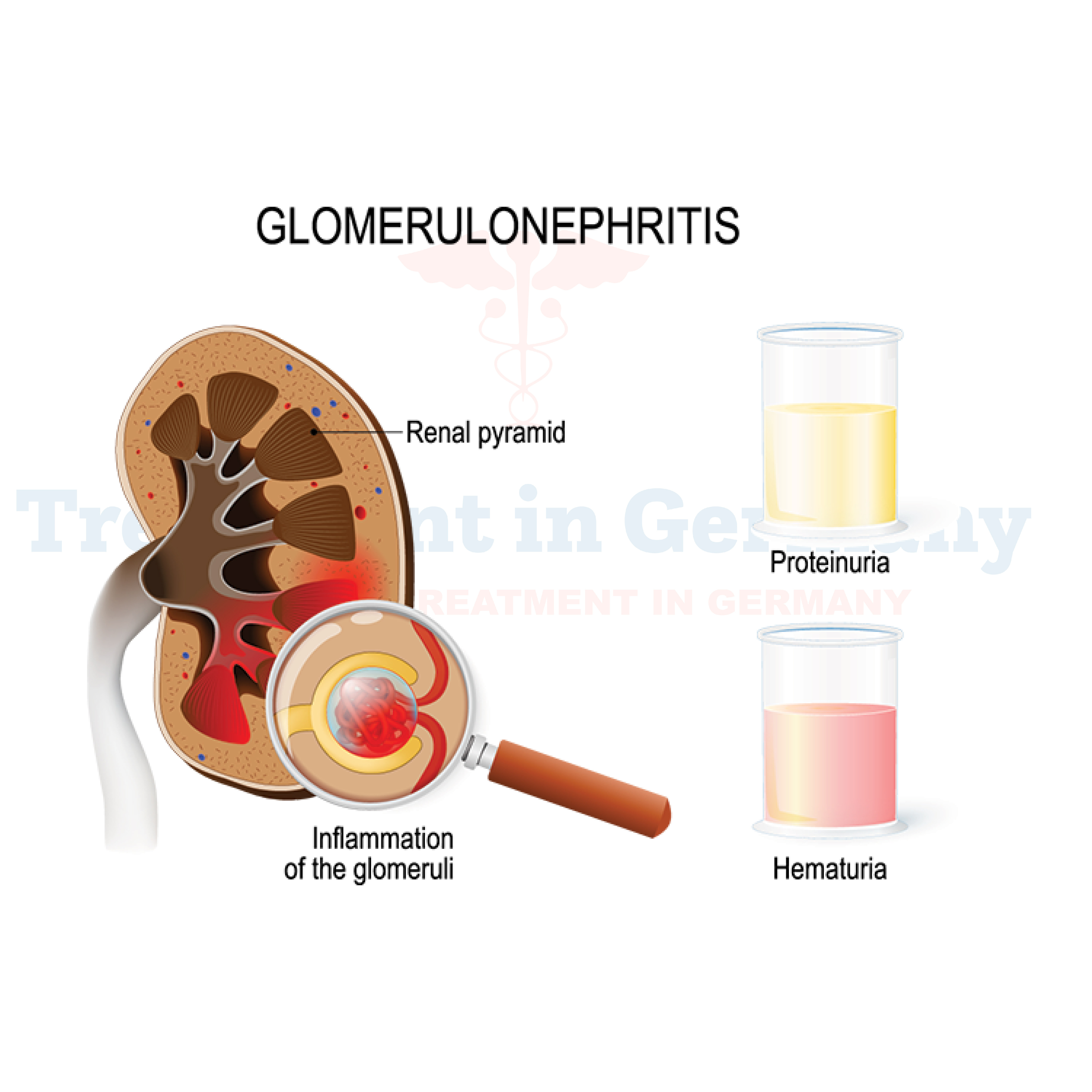
Glomerulonephritis is a kidney condition characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli, which are the tiny filters in the kidneys responsible for removing waste and excess fluids from the blood. When these filters become inflamed, they may not function properly, leading to various complications.
Side Effects of Glomerulonephritis:
The symptoms of glomerulonephritis can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but common signs may include:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria): The inflammation of the glomeruli can cause blood to leak into the urine, resulting in a pink or cola-colored appearance.
- Foamy urine: Protein may leak into the urine due to damaged glomeruli, causing it to appear foamy.
- Swelling (edema): Fluid retention can lead to swelling in the face, hands, feet, and abdomen.
- High blood pressure: Glomerulonephritis can disrupt the body's fluid balance and lead to elevated blood pressure levels.
- Fatigue: Decreased kidney function can result in fatigue and weakness due to the buildup of waste products in the blood.
How is Glomerulonephritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing glomerulonephritis typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including:
- Urinalysis: This test examines a urine sample for abnormalities such as blood, protein, or abnormal levels of waste products.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can assess kidney function by measuring levels of creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN).
- Kidney biopsy: A small sample of kidney tissue may be removed and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of kidney damage.
- Imaging tests: Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to assess the size and structure of the kidneys.
Potential Treatments of Glomerulonephritis:
Treatment for glomerulonephritis aims to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, and preserve kidney function. Depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, treatment options may include:
- Medications: Immunosuppressive drugs, such as corticosteroids or cyclophosphamide, may be prescribed to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation in the kidneys.
- Blood pressure control: Medications to lower blood pressure, such as ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), may be prescribed to help protect the kidneys and reduce proteinuria.
- Dietary changes: Limiting salt, protein, and phosphorus intake may help manage symptoms and reduce strain on the kidneys.
- Dialysis: In advanced cases of glomerulonephritis where kidney function is severely impaired, dialysis may be necessary to remove waste products and excess fluids from the blood.
- Kidney transplant: For patients with end-stage kidney disease, a kidney transplant may be considered as a long-term treatment option to restore kidney function.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
