What is Goiter?
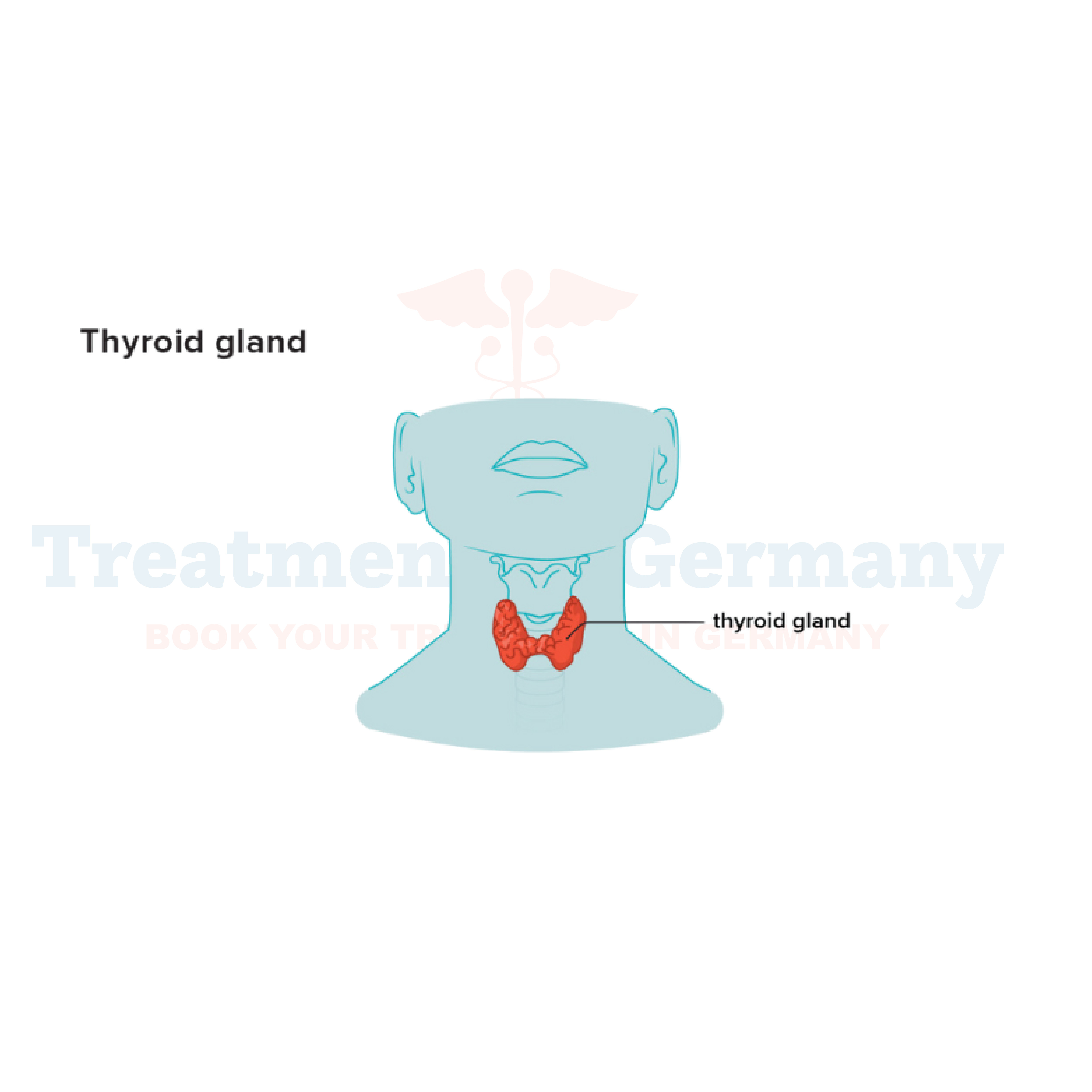
Goiter is a condition characterized by the abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, located in the neck. This enlargement can lead to a visible swelling in the neck area.
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions by producing hormones that control metabolism. When the thyroid gland becomes enlarged, it can disrupt its normal function, resulting in symptoms and complications.
Side Effects of Goiter:
The symptoms of goiter can vary depending on the size and underlying cause of the enlargement. Some common side effects may include:
- Swelling or enlargement of the neck, which may be visible or palpable.
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing, particularly if the goiter is large and presses on surrounding structures.
- Hoarseness or changes in voice, due to compression of the vocal cords by the enlarged thyroid.
- Thyroid dysfunction, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and temperature sensitivity.
- Development of nodules within the thyroid gland, which may require further evaluation for the risk of cancer.
How is Goiter Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Goiter typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. During the physical examination, your healthcare provider will palpate your neck to feel for any swelling or enlargement of the thyroid gland. They may also ask about your symptoms and risk factors.
Diagnostic tests that may be used to evaluate goiter include:
- Thyroid function tests: Blood tests to measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3, T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to assess thyroid function.
- Ultrasound: Imaging technique used to visualize the size, shape, and texture of the thyroid gland, as well as to detect any nodules or abnormalities.
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB): Procedure to collect a small sample of thyroid tissue for examination under a microscope, typically performed if nodules are present to rule out thyroid cancer.
Potential Treatments of Goiter:
Treatment options for Goiter depend on the underlying cause, the size of the enlargement, and the presence of symptoms. Some potential treatments include:
- Medications: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed to normalize hormone levels and shrink the goiter, especially if it's caused by thyroid hormone imbalance.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: A radioactive form of iodine is taken orally, which is absorbed by the thyroid gland and helps shrink the goiter, particularly if it's caused by overactivity of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism).
- Surgery (thyroidectomy): Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary for large or symptomatic goiters, or if there's suspicion of thyroid cancer.
- Observation: In some cases, particularly if the Goiter is small and asymptomatic, your healthcare provider may recommend regular monitoring without immediate intervention.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a
complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
