What is Graves' Disease:
Graves' Disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the thyroid gland, causing it to become overactive, a condition known as hyperthyroidism.
In Graves' Disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to an excessive production of thyroid hormones.
This overproduction of hormones can wreak havoc on various bodily functions and systems, causing a range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person's quality of life.
Side effects of Graves' Disease:
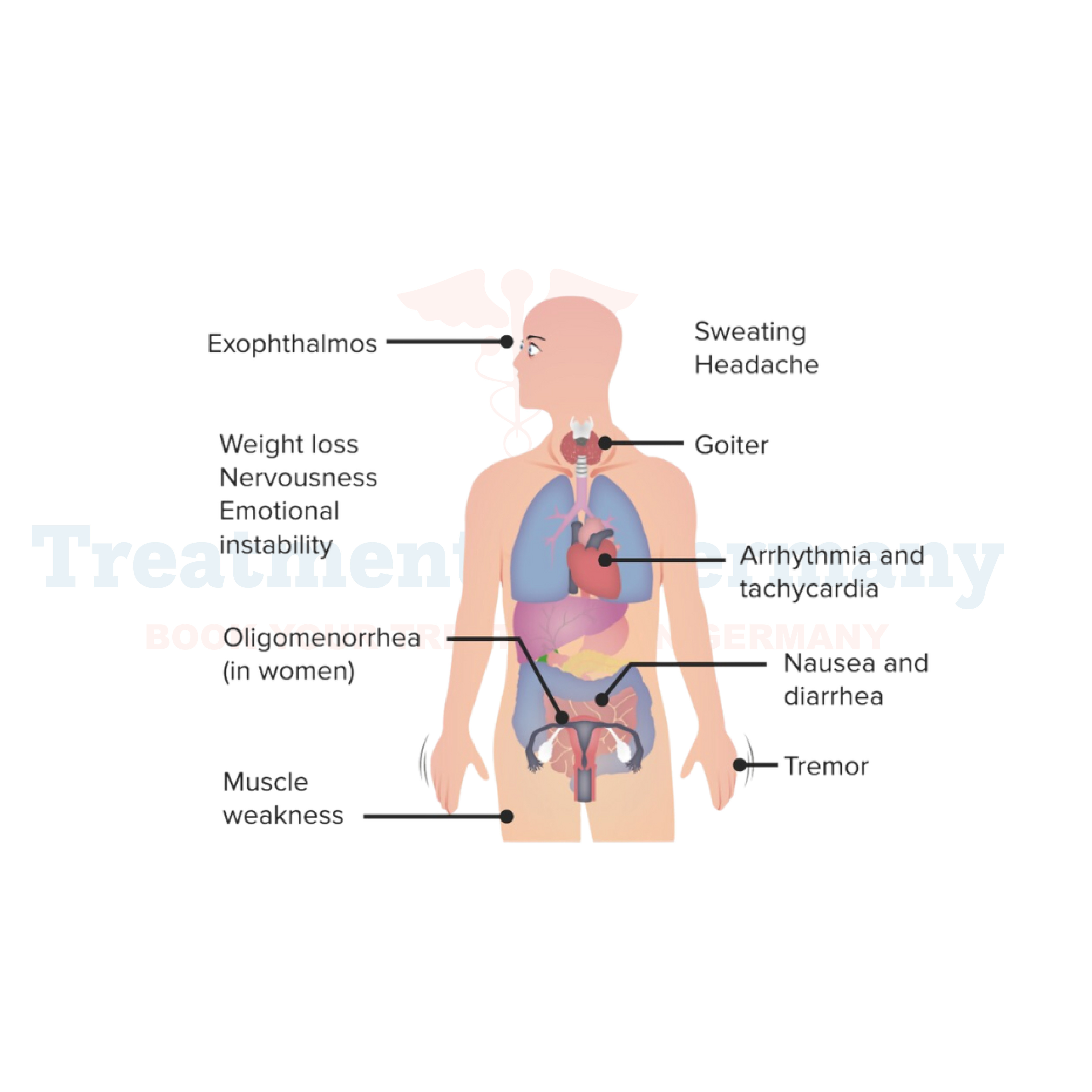
The symptoms of Graves' Disease can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
Left untreated, Graves' Disease can lead to serious complications such as heart problems, osteoporosis, and in severe cases, thyroid storm, a life-threatening condition characterized by extremely high levels of thyroid hormones.
How is Graves' Disease diagnosed?:
Diagnosing Graves' Disease typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Y
our doctor may ask about your symptoms, family history of thyroid disorders, and any other relevant medical conditions. During the physical exam, they may check for signs such as a rapid heartbeat, tremors, or enlarged thyroid gland.
Potential treatments of Graves' Disease:
Treatment for Graves' Disease aims to normalize thyroid hormone levels, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications.
The choice of treatment depends on various factors including the severity of symptoms, age, overall health, and personal preferences. Common treatment options include:
1. Medications: Antithyroid drugs such as methimazole and propylthiouracil (PTU) are often prescribed to block the production of thyroid hormones. These medications can help alleviate symptoms and may be used as a temporary measure before considering other treatment options.
2. Radioactive iodine therapy: Radioactive iodine is taken orally and absorbed by the thyroid gland, where it destroys the overactive thyroid cells. This treatment is often considered a permanent solution for Graves' Disease but may lead to hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) requiring lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
3. Thyroid surgery (thyroidectomy): In cases where medications and radioactive iodine therapy are not suitable or effective, surgical removal of the thyroid gland may be recommended. Thyroidectomy is typically reserved for patients with severe symptoms, large goiters, or those who cannot tolerate other treatments.
4. Beta-blockers: Beta-blockers such as propranolol may be prescribed to manage symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, tremors, and anxiety while awaiting the effects of other treatments.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
