What is Inflammatory Myopathies?
Inflammatory Myopathies, often referred to as idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM), are a group of rare autoimmune disorders that affect skeletal muscles.
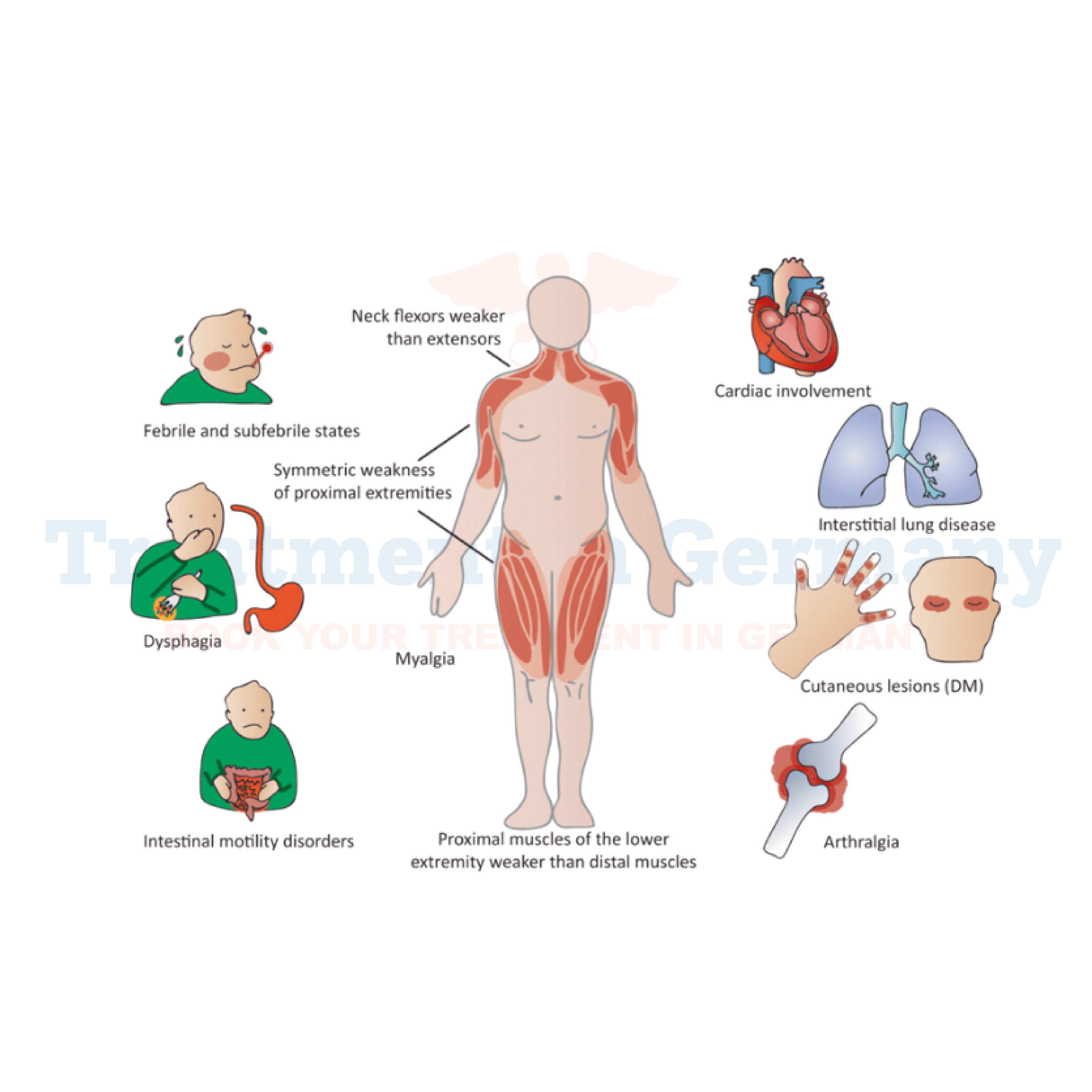
These conditions are characterized by chronic inflammation of the muscles, leading to progressive muscle weakness and in some cases, muscle pain. The exact cause of these conditions is not fully understood, but they are believed to involve an abnormal immune response targeting the muscles themselves.
Side Effects of Inflammatory Myopathies
The primary symptoms of Inflammatory Myopathies include muscle weakness, which can affect mobility and daily activities.
Patients may also experience muscle pain, fatigue, and difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) in some cases. Over time, muscle weakness may lead to complications such as falls or difficulty with breathing and speaking.
How is Inflammatory Myopathies Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Inflammatory Myopathies involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, blood tests to detect specific antibodies associated with these conditions (such as anti-Jo-1 antibodies), electromyography (EMG) to assess electrical activity in muscles, and muscle biopsy to examine muscle tissue for signs of inflammation.
Potential Treatment of Inflammatory Myopathies
Treatment strategies for Inflammatory Myopathies aim to suppress inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and preserve muscle function. In Germany, treatment typically involves a multidisciplinary approach coordinated by rheumatologists, neurologists, and other specialists. Common treatments may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
