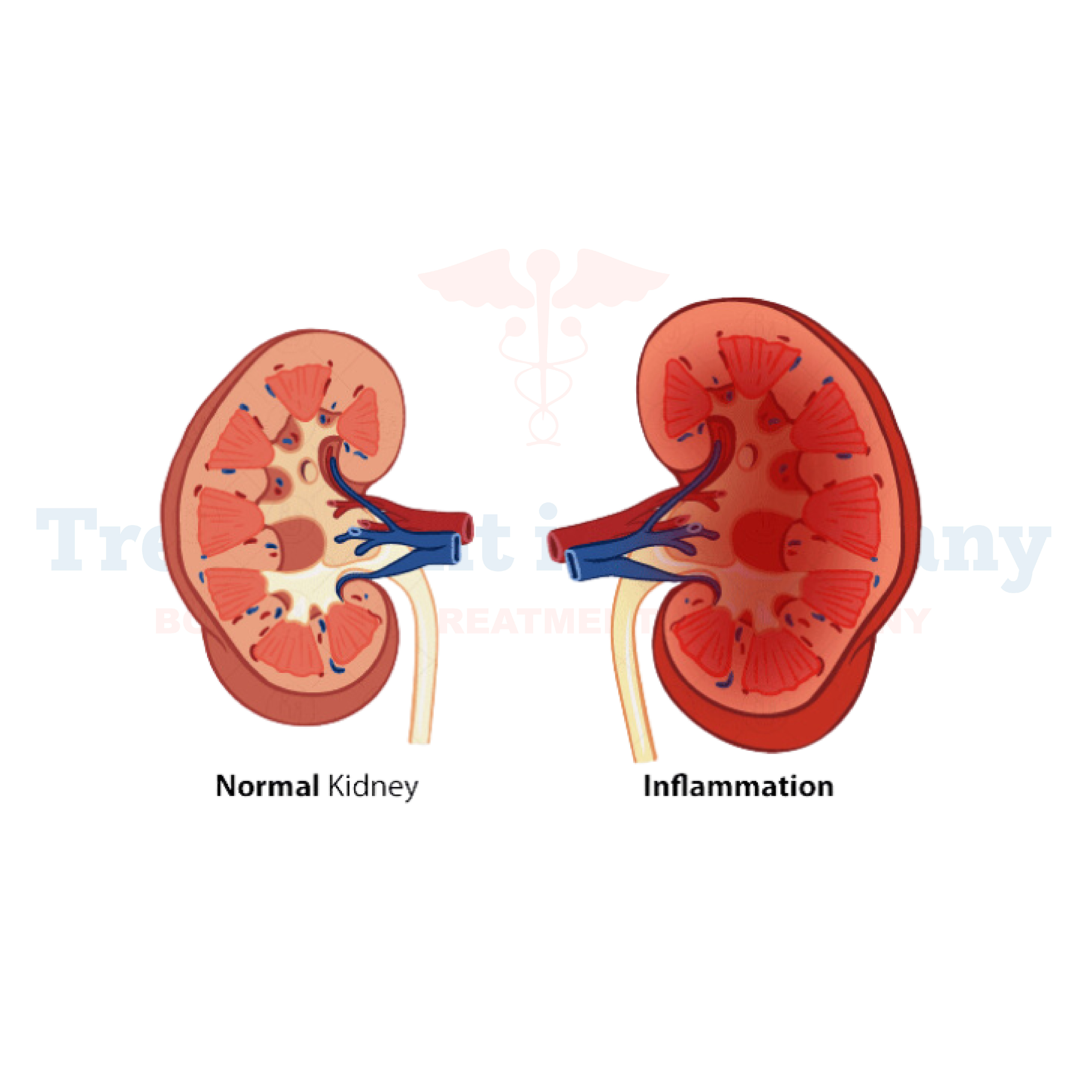
What is Interstitial Nephritis?
Interstitial Nephritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the renal interstitium, which is the tissue surrounding the kidney tubules.
This inflammation can impair kidney function, leading to problems with the body's ability to filter waste and maintain fluid balance.
Side effects of Interstitial Nephritis:
How is Interstitial Nephritis diagnosed?
Potential treatments of Interstitial Nephritis:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
