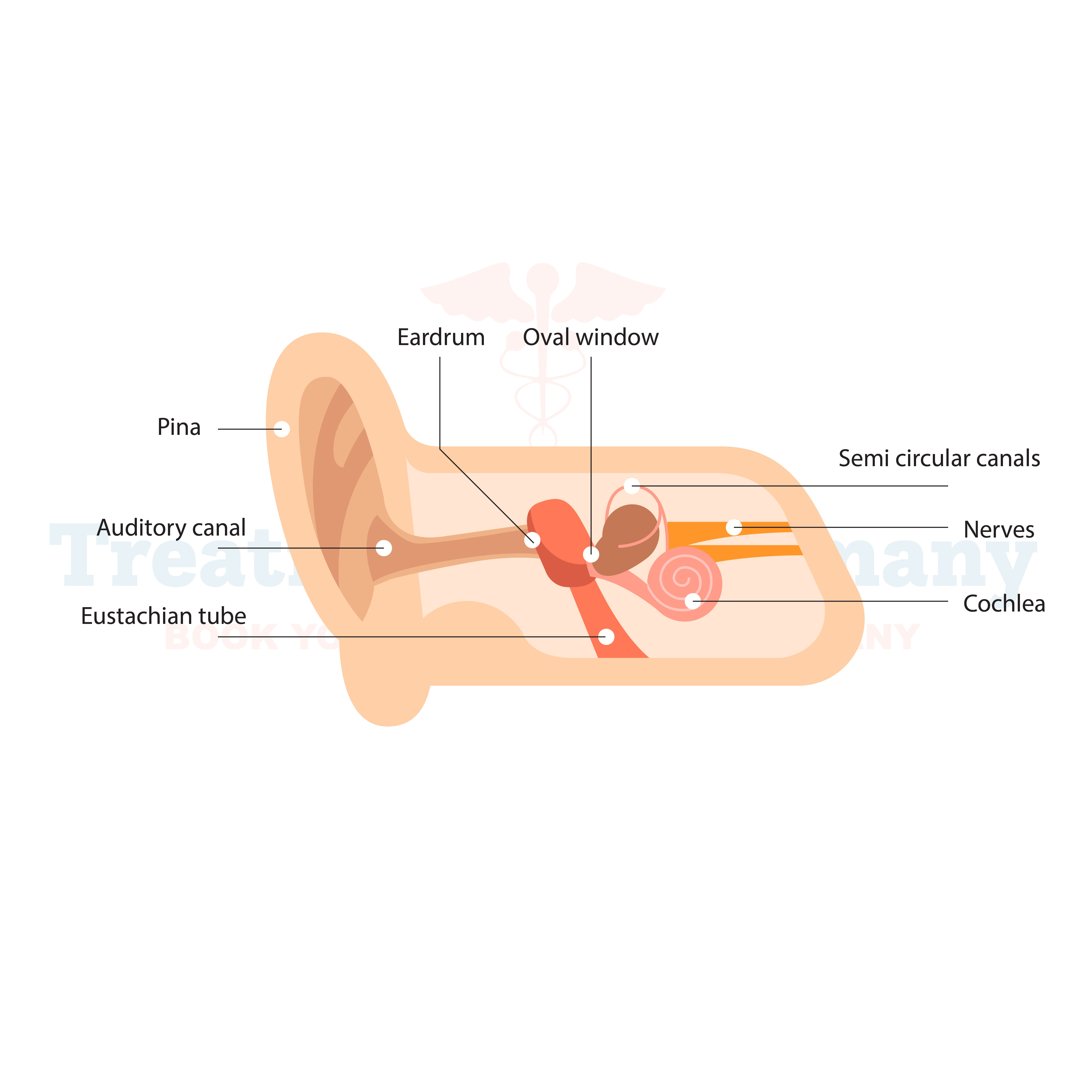
What is Mastoiditis:
Mastoiditis is a serious bacterial infection that affects the mastoid bone, located behind the ear. This condition typically develops as a complication of untreated or poorly treated middle ear infections (otitis media). The mastoid bone contains air cells that can become infected and inflamed, leading to Mastoiditis. It can affect individuals of any age but is more common in children.
Side Effects of Mastoiditis:
The symptoms of Mastoiditis can vary but often include:
How is Mastoiditis Diagnosed?
To diagnose Mastoiditis, your doctor will perform a physical examination and may recommend the following tests:
Potential Treatments of Mastoiditis:
The treatment of Mastoiditis typically involves a combination of antibiotics and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Here are the potential treatments:
1. Antibiotics: If the infection is diagnosed early and is not severe, your doctor may prescribe oral or intravenous antibiotics to fight the bacterial infection. It's crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed.
2. Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help alleviate ear pain and discomfort.
3. Surgical drainage (Mastoidectomy): In severe cases or if the infection does not respond to antibiotics, surgical drainage of the infected mastoid air cells may be necessary. During a mastoidectomy, the infected tissue is removed to prevent further spread of the infection and to improve drainage.
4. Ear tube placement: In some cases, especially in children with recurrent ear infections, your doctor may recommend placing tubes in the ears (tympanostomy tubes) to improve ventilation and drainage and prevent future infections.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive acomplimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
