Myopathy Treatment in Germany
Myopathy refers to a group of neuromuscular disorders that affect muscle function, leading to weakness, fatigue, and impaired movement. These conditions can be inherited (genetic) or acquired due to inflammation, metabolic disorders, or autoimmune reactions. Germany, known for its cutting-edge medical advancements, offers some of the most effective and innovative treatments for myopathy, including regenerative medicine, stem cell therapy, and specialized rehabilitation programs.
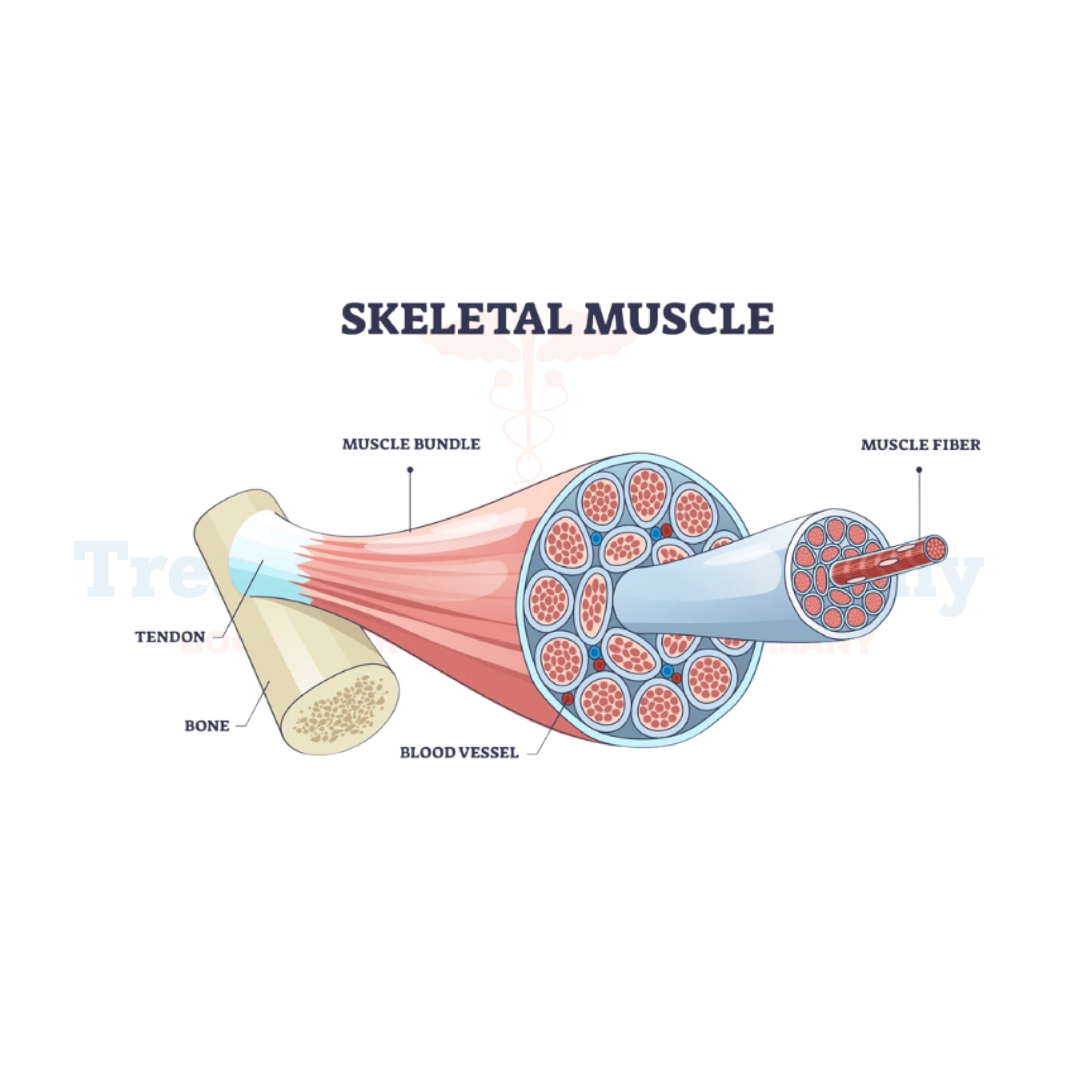
Unlike nerve-related disorders, myopathies primarily affect the muscle fibers themselves, leading to progressive degeneration and loss of strength. Some forms of myopathy are present from birth, while others develop later in life due to genetic mutations, infections, or autoimmune conditions.
Types of Myopathy
Myopathy is classified into different categories based on its cause and progression:
- Congenital Myopathy: Present at birth due to genetic mutations affecting muscle development.
- Muscular Dystrophy: A genetic disorder causing progressive muscle degeneration.
- Inflammatory Myopathy: Includes conditions like polymyositis and dermatomyositis, where the immune system attacks muscle tissues.
- Metabolic Myopathy: Caused by enzyme deficiencies affecting energy production in muscles.
- Toxic or Drug-Induced Myopathy: Triggered by medications, alcohol, or toxins.
- Endocrine Myopathy: Linked to hormonal imbalances, such as thyroid disorders.
- Mitochondrial Myopathy: Resulting from defects in mitochondria, the energy-producing structures in cells.
Causes of Myopathy
The underlying causes of myopathy vary depending on the type:
- Genetic Mutations: Inherited disorders affecting muscle proteins.
- Autoimmune Reactions: The immune system mistakenly attacks muscle tissue.
- Metabolic Disorders: Impaired energy production in muscle cells.
- Inflammation: Chronic muscle inflammation due to infections or immune dysfunction.
- Toxin Exposure: Alcohol, drugs, and environmental toxins can damage muscles.
- Endocrine Disorders: Hormonal imbalances, including hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms of Myopathy
Symptoms vary based on the type and severity of myopathy but commonly include:
- Muscle Weakness: Often affecting the arms, legs, and torso.
- Fatigue: Muscles tire quickly after minimal exertion.
- Difficulty Walking or Standing: Weakness in leg muscles.
- Muscle Cramps or Pain: Often occurs with movement.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): In severe cases.
- Respiratory Problems: If the muscles controlling breathing are affected.
- Joint Stiffness or Contractures: Restricted range of motion.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tools
Germany's advanced healthcare system provides precise diagnostic tools for detecting myopathy:
- Blood Tests: Detect muscle enzyme levels, such as creatine kinase (CK), indicating muscle damage.
- Genetic Testing: Identifies mutations linked to hereditary myopathies.
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures electrical activity in muscles to detect dysfunction.
- Muscle Biopsy: Examines muscle tissue under a microscope for abnormalities.
- MRI and CT Scans: Provide detailed imaging of muscle structure and damage.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: Assess electrical signals in nerves to rule out neuropathic disorders.
Treatment Options for Myopathy in Germany
Germany is at the forefront of myopathy treatment, offering advanced therapies tailored to individual needs.
Medications and Drug Therapies
- Corticosteroids (e.g., Prednisone): Reduce inflammation in autoimmune myopathies.
- Immunosuppressants: Control immune system activity in inflammatory myopathies.
- Gene Therapy: Targeted genetic treatments for hereditary myopathies.
- Metabolic Supplements: Support energy production in metabolic myopathies.
Regenerative Medicine and Advanced Therapies
- Stem Cell Therapy: Studied for its potential to regenerate damaged muscle fibers.
- Dendritic Cell Therapy: Investigated for immune system modulation in autoimmune myopathies.
- TACE (Transarterial Chemoembolization): Being explored as a targeted treatment for immune-related disorders.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
- Muscle Strengthening Exercises: Maintain mobility and function.
- Occupational Therapy: Helps with daily tasks and adaptive equipment.
- Respiratory Therapy: Assists with breathing difficulties.
Surgical and Assistive Treatments
- Orthopedic Surgery: Corrects joint deformities or contractures.
- Bracing and Mobility Aids: Support weakened muscles and improve movement.
- Assistive Devices: Walking aids, wheelchairs, and speech therapy devices.
Why Choose Treatment in Germany?
Germany is a leading destination for myopathy treatment due to:
- World-Class Hospitals: Equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment facilities.
- Experienced Specialists: Neurologists, geneticists, and immunologists with expertise in myopathy care.
- Innovative Therapies: Access to gene therapy, stem cell research, and regenerative medicine.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailored care based on the latest medical advancements.
- Comprehensive Rehabilitation Centers: Focused on long-term muscle maintenance.
Prevention and Management
While some forms of myopathy cannot be prevented, effective management strategies include:
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Monitor symptoms and adjust treatment.
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: Support muscle function and prevent deterioration.
- Avoiding Toxins: Limiting alcohol and medication-induced muscle damage.
- Physical Therapy: Prevents muscle stiffness and maintains flexibility.
- Respiratory Support: Essential for severe cases affecting breathing.
- Genetic Counseling: Helps families understand the risks of inherited myopathies.
Conclusion
Myopathy encompasses a range of muscle disorders that can significantly impact mobility and quality of life. With early diagnosis and innovative treatments, patients can effectively manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Germany’s world-class medical facilities, expert specialists, and access to groundbreaking therapies make it a leading choice for myopathy treatment. By combining medication, regenerative therapies, and comprehensive rehabilitation, Germany offers hope for patients seeking advanced and effective care.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
