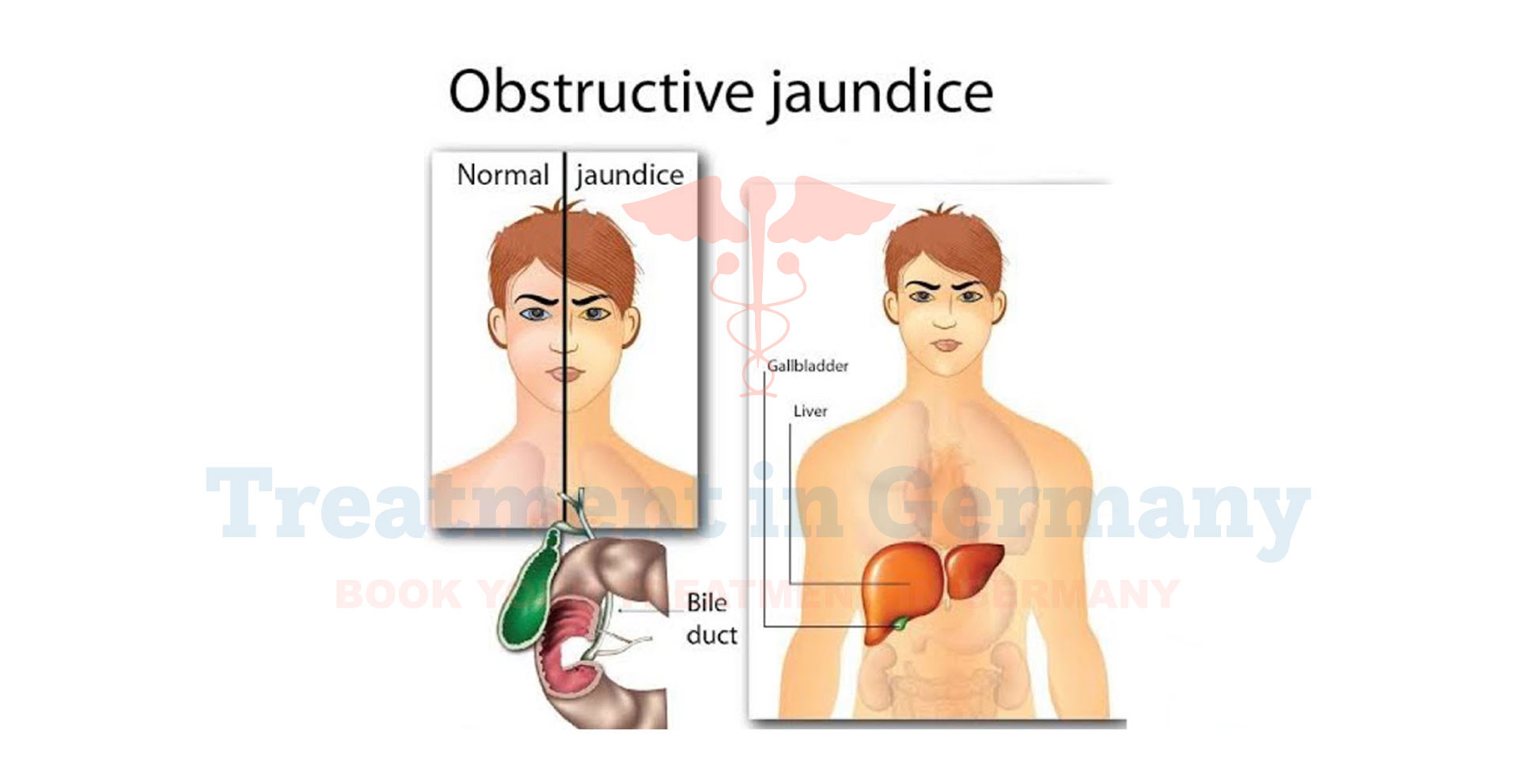
What is Obstructive Jaundice?
Obstructive jaundice is a condition where a blockage in the bile ducts prevents bile from flowing from the liver to the small intestine.
This blockage causes a buildup of bile pigments, particularly bilirubin, in the blood. The excess bilirubin leads to a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes, known as jaundice. This condition can result from various causes, including gallstones, tumors, or strictures in the bile ducts.
Side Effects of Obstructive Jaundice
The primary symptom of obstructive jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and sclera (the white part of the eyes). However, patients may also experience:
- Dark Urine: Due to increased bilirubin being excreted through the kidneys.
- Pale Stools: A lack of bile reaching the intestines can result in lighter-colored stools.
- Itching (Pruritus): Accumulation of bile salts in the blood can lead to intense itching.
- Abdominal Pain: Particularly in the upper right side, if the obstruction is caused by gallstones or inflammation.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These may occur due to the digestive system's disruption.
How is Obstructive Jaundice Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of obstructive jaundice involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will review your symptoms and medical history and perform a physical exam to check for jaundice and abdominal tenderness.
- Blood Tests: These tests measure levels of bilirubin, liver enzymes, and other markers to assess liver function and the extent of bile obstruction.
Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound: Often the first imaging test, it can identify obstructions such as gallstones or tumors.
- CT Scan: Provides a detailed view of the bile ducts and surrounding structures.
- MRI or MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography): Offers a non-invasive view of the bile ducts.
Endoscopic Procedures:
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): Allows visualization and possible removal of blockages in the bile ducts.
- PTC (Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography): Used when ERCP is not feasible, this procedure involves injecting a contrast dye into the bile ducts through a needle inserted into the liver.
Potential Treatment of Obstructive Jaundice
Treatment for obstructive jaundice focuses on addressing the underlying cause of the obstruction and alleviating symptoms:
- Medication: In some cases, medications may be used to manage symptoms or treat underlying conditions, such as antibiotics for infections or medications to dissolve gallstones.
Surgical Intervention:
- Cholecystectomy: Surgical removal of the gallbladder may be required if gallstones are causing the obstruction.
- Biliary Stenting or Drainage: Placement of a stent to keep the bile duct open or creating a bypass to allow bile flow around the obstruction.
- Endoscopic Procedures: As mentioned, ERCP can be used to remove obstructions or place stents to relieve the blockage.
- Supportive Care: Managing symptoms like itching and pain through medications and lifestyle adjustments is crucial.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
