What is Pediatric Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)?
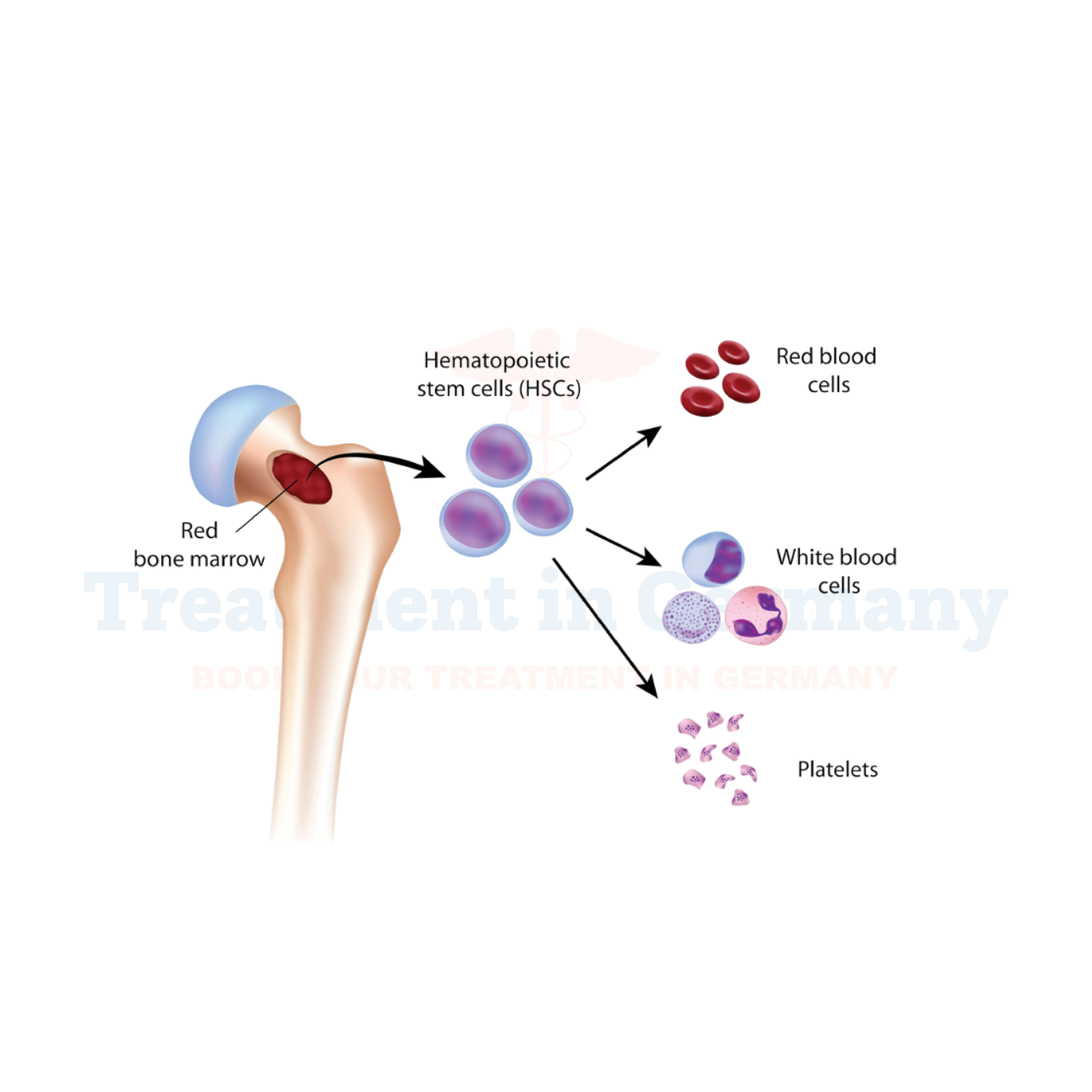
Pediatric Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) are a group of rare disorders characterized by abnormal development of blood cells in the bone marrow.
In children, this condition affects the production of healthy blood cells, leading to insufficient or dysfunctional blood cells being released into the bloodstream.
Side Effects of Pediatric Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
Children with Pediatric Myelodysplastic Syndromes may experience a range of symptoms and complications due to insufficient functioning of their blood cells. Common side effects include:
These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the type and progression of MDS in each child.
How is Pediatric Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Pediatric Pediatric Myelodysplastic Syndromes involves several steps to assess blood cell counts, bone marrow function, and genetic markers:
These diagnostic tools allow healthcare providers to determine the type and severity of MDS in pediatric patients.
Potential Treatment of Pediatric Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
Treatment options for Pediatric Pediatric Myelodysplastic Syndromes aim to manage symptoms, improve blood cell production, and potentially cure the condition. Depending on the child's age, overall health, and specific subtype of MDS, treatment may include:
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
