What is Sjögren's Syndrome?
Sjögren's Syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the moisture-producing glands in your body.
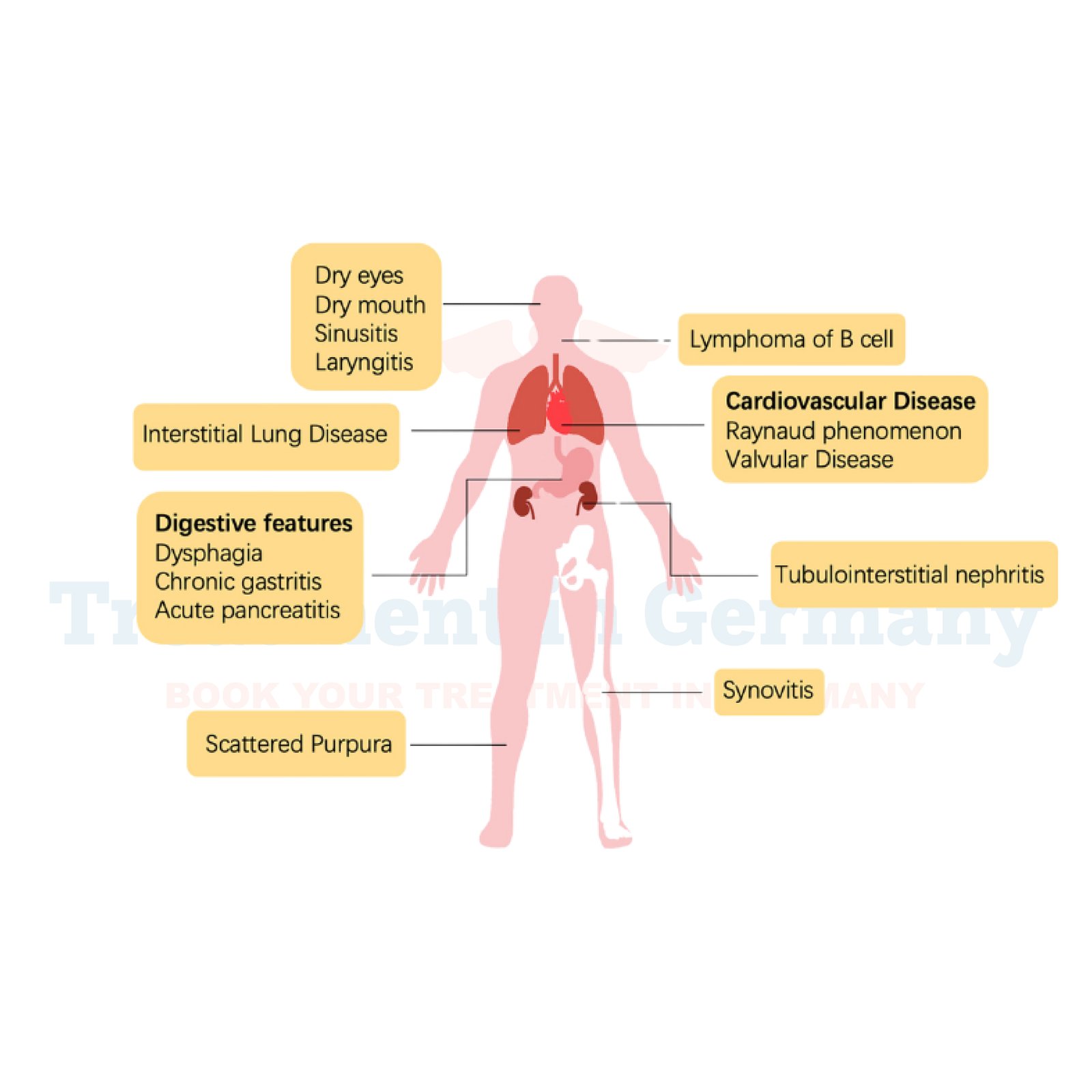
This condition leads to dry mouth (xerostomia) and dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitis sicca), but it can also impact other parts of the body. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, which can cause inflammation and damage in the affected glands.
Side Effects of Sjögren's Syndrome
The side effects of Sjögren's Syndrome can vary widely but commonly include:
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): This can lead to difficulty speaking, swallowing, and tasting food, as well as an increased risk of dental decay and oral infections.
- Dry Eyes (Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca): Symptoms include a gritty or burning sensation, redness, and sensitivity to light. It can also cause increased risk of eye infections.
- Joint Pain: Many patients experience discomfort and swelling in their joints.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness that can affect daily activities and quality of life.
- Vaginal Dryness: Women may experience discomfort and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Swelling of Salivary Glands: Particularly noticeable in the cheeks and jaw area.
In some cases, Sjögren's Syndrome can lead to complications affecting other organs, such as the kidneys, liver, or lungs, and may increase the risk of lymphoma.
How is Sjögren's Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Sjögren's Syndrome involves a combination of methods:
- Medical History and Symptoms Review: A detailed assessment of symptoms and medical history is essential. Your doctor will inquire about dryness in your mouth and eyes, as well as any other related symptoms.
- Physical Examination: Your doctor will conduct a physical examination to check for signs of dry eyes and mouth, and other potential indicators of the syndrome.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify specific autoantibodies commonly associated with Sjögren's Syndrome, such as anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La antibodies.
- Eye Tests: Tests like the Schirmer's test measure tear production, while other exams assess the health of your cornea and conjunctiva.
- Salivary Gland Biopsy: A small sample of tissue from a salivary gland may be taken to look for characteristic inflammation.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be used to evaluate the condition of the salivary glands.
Potential Treatment of Sjögren's Syndrome
While there is no cure for Sjögren's Syndrome, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
Symptom Management:
- Artificial Tears and Eye Lubricants: These help relieve dry eyes and protect the eye surface.
- Saliva Substitutes: Gels and sprays can help alleviate dry mouth.
- Oral Hygiene Products: Fluoride treatments and regular dental check-ups are crucial to prevent tooth decay and manage oral health.
Medications:
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help with joint pain and inflammation.
- Immunosuppressive Medications: Drugs like hydroxychloroquine or methotrexate may be prescribed to reduce immune system activity and inflammation.
- Cholinergic Agents: Medications like pilocarpine can stimulate saliva production.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water and using saliva stimulants can help manage dry mouth.
- Humidifiers: Adding moisture to the air can ease dry eyes and respiratory discomfort.
- Regular Exercise and Rest: Balancing activity with rest can help manage fatigue and joint pain.
Supportive Therapies:
- Counseling and Support Groups: Connecting with others who have Sjögren’s Syndrome can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Specialist Care: Regular consultations with rheumatologists and ophthalmologists ensure comprehensive management of the syndrome and its complications.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
