What are Urinary Tract Infections (Recurrent and Complicated)?
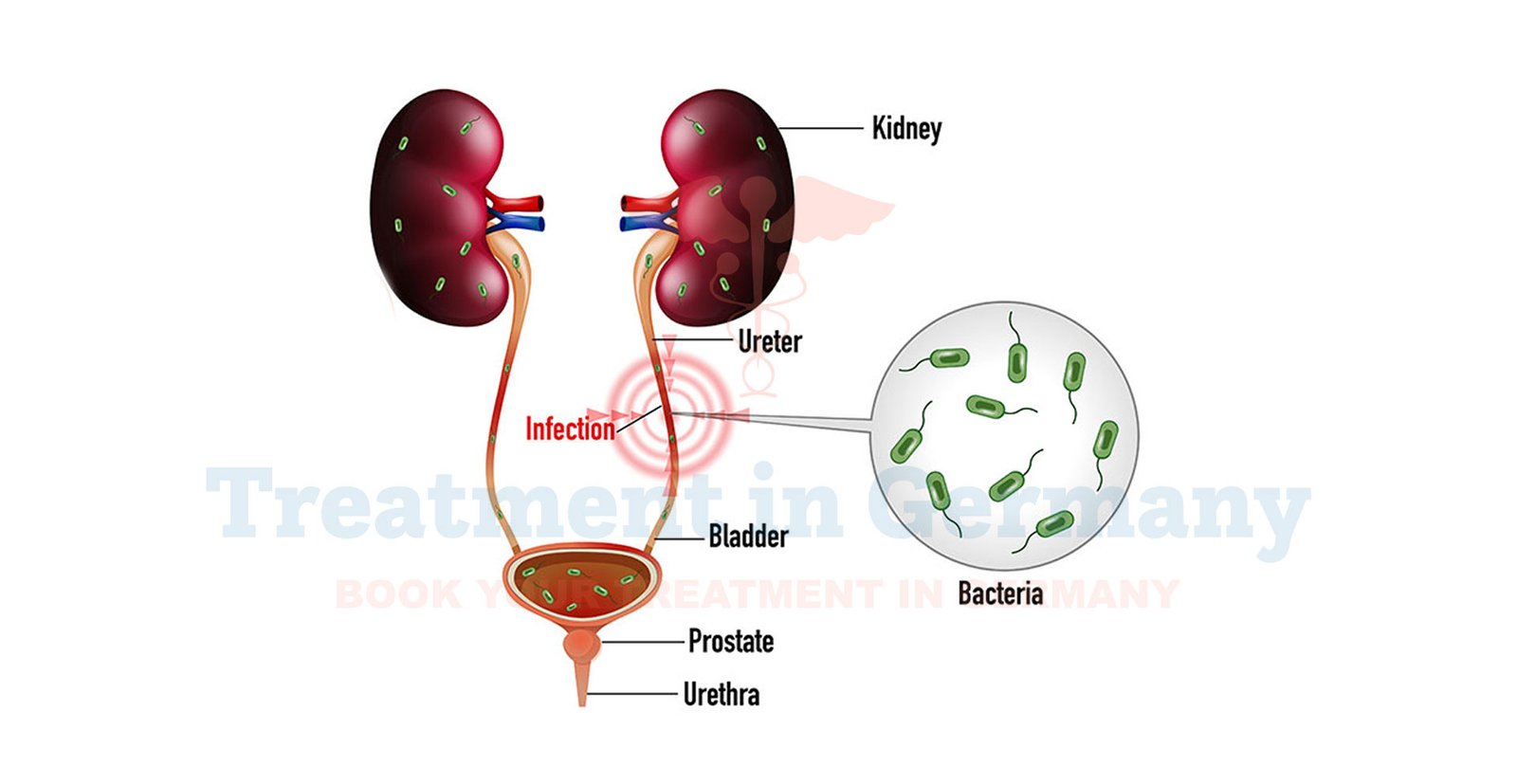
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) occur when bacteria enter and multiply in the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Recurrent UTIs are infections that return multiple times, often within a short period. Complicated UTIs are more severe and may involve structural abnormalities, underlying health conditions, or resistance to antibiotics, making them harder to treat.
Side Effects of Urinary Tract Infections (Recurrent and Complicated)
Recurrent and complicated Urinary tract infections can lead to a range of unpleasant and sometimes severe symptoms. These may include:
- Frequent Urination: The need to urinate often, even if only small amounts of urine are produced.
- Burning Sensation: Pain or a burning feeling during urination.
- Lower Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area.
- Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine: Changes in the appearance or odor of urine.
- Fever and Chills: Especially in complicated cases, indicating a more severe infection.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Which may accompany fever and indicate the infection has reached the kidneys.
In severe cases, complications such as kidney damage or sepsis (a systemic infection) may occur, leading to more serious health issues.
How is Urinary Tract Infections (Recurrent and Complicated) Diagnosed?
Diagnosing recurrent and complicated Urinary tract infections typically involves a combination of methods:
- Medical History and Symptoms Review: Discussing your symptoms and medical history with a healthcare provider.
- Urine Tests: A urine sample is analyzed to identify the presence of bacteria, white blood cells, or other signs of infection. This may include a urinalysis and a urine culture to determine the specific type of bacteria and its antibiotic sensitivities.
- Imaging Studies: For complicated UTIs, imaging tests such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to detect structural abnormalities or complications within the urinary tract.
- Cystoscopy: In some cases, a flexible tube with a camera (cystoscope) is inserted into the urethra to directly view the bladder and urethra.
Potential Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections (Recurrent and Complicated)
Treatment for recurrent and complicated Urinary tract infections in Germany generally includes:
- Antibiotics: A course of antibiotics is prescribed based on the specific bacteria identified. In complicated cases, a longer or different antibiotic regimen may be necessary.
- Increased Fluid Intake: Drinking plenty of fluids helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Pain Relief: Medications may be recommended to manage pain and discomfort.
- Addressing Underlying Conditions: For complicated UTIs, treating any underlying health issues or structural abnormalities is crucial. This may involve surgical interventions or management of chronic conditions.
- Preventive Measures: To prevent recurrence, strategies may include lifestyle modifications, such as drinking more fluids, practicing good hygiene, and, in some cases, using preventive antibiotics or other medications.
👉 Contact us for further information and receive a complimentary consultation.

.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)


.webp)
 (1).webp)

.webp)
 (1).webp)
